Shuangtengbitong tincture treatment of collagen-induced arthritis via downregulation of the expression of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB
- PMID: 23403612
- PMCID: PMC3570159
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.853
Shuangtengbitong tincture treatment of collagen-induced arthritis via downregulation of the expression of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB
Abstract
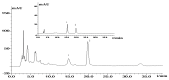
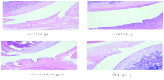
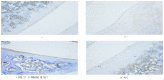
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease and may lead to joint damage, synovial membrane destruction and cartilage and bone damage. RA is closely associated with increased expression of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB). Therefore, inhibition of the expression of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB is a promising strategy for the development of novel anti-RA therapies. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of shuangtengbitong tincture (STBT) on the expression of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB in synovial tissues of rats with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). STBT as a clinical prescription created at Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCM) Affiliated People's Hospital has been shown to be clinically effective in the treatment of RA. The model of Wistar rats with CIA was created using bovine type II collagen. The two treatment groups with CIA were administered STBT (1 ml per time) or Votalin (∼1 cm per time) for ∼1 month continuously. Following treatment, STBT suppressed paw swelling significantly (P<0.05) compared with the model group. STBT also improved pathological changes, STBT-treated rats showed a significant improvement in synovial hyperplasia, inflammatory infiltration, cartilage and bone destruction and other symptoms. The protein expression levels of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB were markedly suppressed in synovial tissues of STBT-treated and Votalin-treated rats. Our findings demonstrate for the first time that STBT markedly reduces paw swelling, improves pathological changes and increases the expression of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and NF-κB in synovial tissues of CIA rats, which may partially explain the anti-RA activity of STBT.
Keywords: interleukin-6; interleukin-8; nuclear transcription factor-κB; rheumatoid arthritis; shuangtengbitong tincture; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures

References
-
- Helliwell P, Woodburn J, Redmond A, Turner D, Davys H. Current concepts in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Helliwell P, Woodburn J, Redmond A, Turner D, Davys H, editors. The Foot and Ankle in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh: 2007. pp. 1–16.
-
- Yang M, Xiao C, Wu Q, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Sanshuibaihu decoction may be associated with nuclear factor-kappa B and p38 MAPK alpha in collagen-induced arthritis in rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;127:264–273. - PubMed
-
- Brenner M, Meng HC, Yarlett NC, et al. The non-MHC quantitative trait locus Cia5 contains three major arthritis genes that differentially regulate disease severity, pannus formation, and joint damage in collagen- and pristane-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2005;174:7894–7903. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Michaud K, Gefeller O, Choi HK. Predicting mortality in patients with rheumatoldarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:1530–1542. - PubMed
-
- Choi EM, Kim YH. Hesperetin attenuates the highly reducing sugar-triggered inhibition of osteoblast differentiation. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2008;24:225–231. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
