The risk of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2
- PMID: 23403622
- PMCID: PMC3624940
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-10-463166
The risk of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2
Abstract
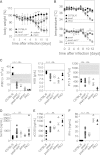
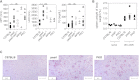
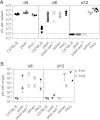
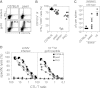
Genetic disorders of lymphocyte cytotoxicity predispose patients to hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Reduced lymphocyte cytotoxicity has been demonstrated in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2 (HPS2), but only a single patient was reported who developed HLH. Because that patient also carried a potentially contributing heterozygous RAB27A mutation, the risk for HLH in HPS2 remains unclear. We analyzed susceptibility to HLH in the pearl mouse model of HPS2. After infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, pearl mice developed all key features of HLH, linked to impaired virus control caused by a moderate defect in CTL cytotoxicity in vivo. However, in contrast to perforin-deficient mice, the disease was transient, and all mice fully recovered and controlled the infection. An additional heterozygous Rab27a mutation did not aggravate the cytotoxicity defect or disease parameters. In the largest survey of 22 HPS2 patients covering 234 patient years, we identified only 1 additional patient with HLH and 2 with incomplete transient HLH-like episodes, although cytotoxicity or degranulation was impaired in all 16 patients tested. HPS2 confers a risk for HLH that is lower than in Griscelli or Chediak-Higashi syndrome, probably because of a milder defect in cytotoxicity. Preemptive hematopoietic stem cell transplantation does not appear justified in HPS2.
Figures


References
-
- Hermansky F, Pudlak P. Albinism associated with hemorrhagic diathesis and unusual pigmented reticular cells in the bone marrow: report of two cases with histochemical studies. Blood. 1959;14(2):162–169. - PubMed
-
- Shotelersuk V, Dell’Angelica EC, Hartnell L, et al. A new variant of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome due to mutations in a gene responsible for vesicle formation. Am J Med. 2000;108(5):423–427. - PubMed
-
- Badolato R, Parolini S. Novel insights from adaptor protein 3 complex deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(4):735–741. quiz 742-733. - PubMed
-
- Clark R, Griffiths GM. Lytic granules, secretory lysosomes and disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15(5):516–521. - PubMed
-
- Enders A, Zieger B, Schwarz K, et al. Lethal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type II. Blood. 2006;108(1):81–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

