The rs11705701 G>A polymorphism of IGF2BP2 is associated with IGF2BP2 mRNA and protein levels in the visceral adipose tissue - a link to type 2 diabetes susceptibility
- PMID: 23403707
- PMCID: PMC3700024
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2012.9.112
The rs11705701 G>A polymorphism of IGF2BP2 is associated with IGF2BP2 mRNA and protein levels in the visceral adipose tissue - a link to type 2 diabetes susceptibility
Abstract
Background: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) regulates translation of IGF2, a growth factor that plays a key role in controlling fetal growth and organogenesis including adipogenesis and pancreatic development. In Caucasians, the rs4402960 G>T polymorphism of IGF2BP2 has been shown to predispose to type 2 diabetes (T2D) in multiple populations. In this study, we tested whether rs4402960 G>T and rs11705701 G>A contribute to the development of T2D in a Russian population.
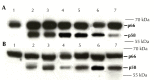
Methods: Both markers were genotyped in Russian diabetic (n = 1,470) and non-diabetic patients (n = 1,447) using a Taqman allele discrimination assay. The odds ratio (OR) for the risk of developing T2D was calculated using logistic regression assuming an additive genetic model adjusted for age, sex, HbA1c, hypertension, obesity, and body mass index (BMI). Multivariate linear regression analyses were used to test genotype-phenotype correlations, and adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, obesity, and BMI. Expression of IGF2BP2 in the visceral adipose tissue was quantified using real-time PCR. The content of IGF2BP2 protein and both its isoforms (p58 and p66) in the adipose tissue was measured using Western blot analysis.
Results: There was no significant association between rs4402960 and T2D. Whereas, allele A of rs11705701 was associated with higher T2D risk (OR = 1.19, p < 0.001). Diabetic and non-diabetic carriers of genotype TT (rs4402960) had significantly increased HOMA-IR (p = 0.033 and p = 0.031, respectively). Non-diabetic patients homozygous for AA (rs11705701) had higher HOMA-IR (p = 0.04), lower HOMA-β (p = 0.012), and reduced 2-h insulin levels (p = 0.016). Non-obese individuals (diabetic and non-diabetic) homozygous for either AA (rs11705701) or TT (rs4402960) had higher levels of IGF2BP2 mRNA in the adipose tissue than other IGF2BP2 variants. Also, allele A of rs11705701 was associated with reduced amounts of the short isoform (p58) and increased levels of the long isoform (p66) of the IGF2BP2 protein in adipose tissue of non-obese diabetic and non-diabetic subjects.
Conclusions: IGF2BP2 genetic variants contribute to insulin resistance in Russian T2D patients. The short protein isoform p58 of IGF2BP2 is likely to play an anti-diabetogenic role in non-obese individuals.
Figures
References
-
- Nielsen FC, Nielsen J, Kristensen MA, Koch G, Christiansen J. Cytoplasmic trafficking of IGF-II mRNA-binding protein by conserved KH domains. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:2087–2097. - PubMed
-
- Jonson L, Vikesaa J, Krogh A, Nielsen LK, Hansen T, Borup R, Johnsen AH, Christiansen J, Nielsen FC. Molecular composition of IMP1 ribonucleoprotein granules. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:798–811. - PubMed
-
- Keene JD, Tenenbaum SA. Eukaryotic mRNPs may represent posttranscriptional operons. Mol Cell. 2002;9:1161–1167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
