Metabolomic changes in gastrointestinal tissues after whole body radiation in a murine model
- PMID: 23403731
- PMCID: PMC3601576
- DOI: 10.1039/c3mb25454b
Metabolomic changes in gastrointestinal tissues after whole body radiation in a murine model
Abstract
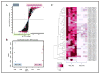
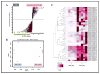
Exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) elicits a set of complex biological responses involving gene expression and protein turnover that ultimately manifest as dysregulation of metabolic processes representing the cellular phenotype. Although radiation biomarkers have been reported in urine and serum, they are not informative about IR mediated tissue or organ specific injury. In the present study we report IR induced metabolic changes in gastrointestinal (GI) tissue of CD2F1 mice using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with electrospray time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Post-radiation GI injury is a critical determinant of survival after exposure to IR. Our results show a distinct dose and time dependent response to GI tissue injury.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
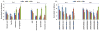

Similar articles
-
Targeted Metabolomics Reveals Metabolomic Signatures Correlating Gastrointestinal Tissue to Plasma in a Mouse Total-body Irradiation Model.Health Phys. 2019 Apr;116(4):473-483. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000955. Health Phys. 2019. PMID: 30624349 Free PMC article.
-
Early metabolic characterization of brain tissues after whole body radiation based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in a rat model.Biomed Chromatogr. 2019 Mar;33(3):e4448. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4448. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Biomed Chromatogr. 2019. PMID: 30499600
-
Proteomic Evaluation of the Acute Radiation Syndrome of the Gastrointestinal Tract in a Murine Total-body Irradiation Model.Health Phys. 2019 Apr;116(4):516-528. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000951. Health Phys. 2019. PMID: 30624357 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Analysis of Mice Exposed to Gamma Radiation Reveals a Systemic Understanding of Total-Body Exposure.Radiat Res. 2017 May;187(5):612-629. doi: 10.1667/RR14592.1. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Radiat Res. 2017. PMID: 28467754 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics in Radiation-Induced Biological Dosimetry: A Mini-Review and a Polyamine Study.Biomolecules. 2018 May 29;8(2):34. doi: 10.3390/biom8020034. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 29844258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor suppressor RARRES1- A novel regulator of fatty acid metabolism in epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 17;13(12):e0208756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208756. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30557378 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Instability and Carcinogenesis of Heavy Charged Particles Radiation: Clinical and Environmental Implications.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Sep 13;55(9):591. doi: 10.3390/medicina55090591. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31540340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Metabolomics Reveals Metabolomic Signatures Correlating Gastrointestinal Tissue to Plasma in a Mouse Total-body Irradiation Model.Health Phys. 2019 Apr;116(4):473-483. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000955. Health Phys. 2019. PMID: 30624349 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation exposure induces cross-species temporal metabolic changes that are mitigated in mice by amifostine.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 7;11(1):14004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93401-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34234212 Free PMC article.
-
One-carbon metabolism and ionizing radiation: a multifaceted interaction.Biomol Concepts. 2017 May 24;8(2):83-92. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2017-0003. Biomol Concepts. 2017. PMID: 28574375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Waselenko JK, MacVittie TJ, Blakely WF, Pesik N, Wiley AL, Dickerson WE, Tsu H, Confer DL, Coleman CN, Seed T, Lowry P, Armitage JO, Dainiak N. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:1037–1051. - PubMed
-
- Budhwar R, Bihari V, Mathur N, Srivastava A, Kumar S. Biomarkers : biochemical indicators of exposure, response, and susceptibility to chemicals. 2003;8:162–166. - PubMed
-
- Porciani S, Lanini A, Balzi M, Faraoni P, Becciolini A. Phys Med. 2001;17(Suppl 1):187–188. - PubMed
-
- Amundson SA, Grace MB, McLeland CB, Epperly MW, Yeager A, Zhan Q, Greenberger JS, Fornace AJ., Jr Cancer Res. 2004;64:6368–6371. - PubMed
-
- Kang CM, Park KP, Song JE, Jeoung DI, Cho CK, Kim TH, Bae S, Lee SJ, Lee YS. Radiat Res. 2003;159:312–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

