Formulation and cytotoxicity evaluation of new self-emulsifying multiple W/O/W nanoemulsions
- PMID: 23403891
- PMCID: PMC3569110
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S35661
Formulation and cytotoxicity evaluation of new self-emulsifying multiple W/O/W nanoemulsions
Abstract
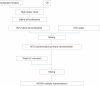
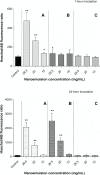
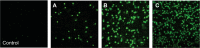
Three multiple water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) nanoemulsions have been designed for potential inclusion of either lipophilic or hydrophilic drugs using a two-step emulsification process exclusively based on low-energy self-emulsification. The W/O primary emulsion was constituted by a blend of oil (medium chain triglyceride), a mixture (7:3) of two surfactants, and a 10% water phase. The surfactants were a mixture of Polysorbate-85/Labrasol(®), Polysorbate-85/Cremophor(®) EL or glycerol/Polysorbate-85. The final W/O/W nanoemulsions were obtained by the addition of water, with a weight ratio nanoemulsion/water of 1:2. The multiple emulsion stability was found to increase from 24 hours to 2 and 6 months with Labrasol, glycerol, and Cremophor, respectively. Cytotoxicity was found for formulations including Labrasol and Cremophor EL. The concentration of emulsion inhibiting 50% cell viability (IC(50)) was determined using the alamarBlue(®) test, giving after 24 hours of incubation, IC(50) = 10.2 mg/mL for the Labrasol formulation and IC(50) = 11.8 mg/mL for the Cremophor EL formulation. Corresponding calculated IC(50) values for surfactants were 0.51 mg/mL for Labrasol and 0.59 mg/mL for Cremophor EL. In both cases, cytotoxicity was due to an apoptotic mechanism, evidenced by chromatin condensation and P2X7 cell death receptor activation. The formulation including glycerol, investigated between 1 and 100 mg/mL concentration of nanoemulsion, did not affect cell viability. Moreover, neither chromatin condensation nor P2X7 activation was found between the 10 and 30 mg/mL final concentration of the emulsion. This last formulation would therefore be of major interest for further developments.
Keywords: Cremophor EL; Labrasol; P2X7 receptor; apoptosis; glycerol; polysorbate.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Formulation development and bioavailability evaluation of a self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system of oleanolic acid.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(1):172-82. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9190-9. Epub 2009 Feb 18. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009. PMID: 19224372 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of cosurfactants and oils on the formation of pharmaceutical microemulsions based on PEG-8 caprylic/capric glycerides.Int J Pharm. 2008 Mar 20;352(1-2):231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.10.041. Epub 2007 Nov 4. Int J Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18068919
-
Biopharmaceutical evaluation of surface active ophthalmic excipients using in vitro and ex vivo corneal models.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jul 30;120:133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.04.032. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29702232
-
Oral self-nanoemulsifying formulation of GLP-1 agonist peptide exendin-4: development, characterization and permeability assesment on Caco-2 cell monolayer.Amino Acids. 2021 Jan;53(1):73-88. doi: 10.1007/s00726-020-02926-0. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33398527
-
Ophthalmic Nanoemulsions: From Composition to Technological Processes and Quality Control.Mol Pharm. 2021 Oct 4;18(10):3719-3740. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00650. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34533317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the P2X7 Receptor in Ocular Stresses: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Vision (Basel). 2017 May 17;1(2):14. doi: 10.3390/vision1020014. Vision (Basel). 2017. PMID: 31740640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced oral absorption of pemetrexed by ion-pairing complex formation with deoxycholic acid derivative and multiple nanoemulsion formulations: preparation, characterization, and in vivo oral bioavailability and anticancer effect.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jun 6;13:3329-3351. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S167958. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29922055 Free PMC article.
-
Coconut Oil Nanoemulsion Loaded with a Statin Hypolipidemic Drug for Management of Burns: Formulation and In Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 7;12(11):1061. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111061. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33171816 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Approach of Targeting Linezolid Nanoemulsion for the Management of Lymph Node Tuberculosis.ACS Omega. 2022 Apr 25;7(18):15688-15694. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00592. eCollection 2022 May 10. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35571844 Free PMC article.
-
Development and in vitro Evaluation of Gastro-protective Aceclofenac-loaded Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jul 23;15:5217-5226. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S250242. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32801687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delmas T, Piraux H, Couffin AC, et al. How to prepare and stabilize very small nanoemulsions. Langmuir. 2011;27(5):1683–1692. - PubMed
-
- Koo OM, Rubinstein I, Onyuksel H. Role of nanotechnology in targeted drug delivery and imaging: a concise review. Nanomedicine. 2005;1(3):193–212. - PubMed
-
- Ravi Theaj Prakash U, Thiagarajan P. Nanoemulsion for drug delivery through different routes. Res Biotechnol. 2011;2(3):1–13.
-
- Matsuzawa A, Morishita M, Takayama K, Nagai T. Absorption of insulin using water-in-oil-in-water emulsion from an enteral loop in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 1995;18(12):1718–1723. - PubMed
-
- Chuan YP, Zeng BY, O’Sullivan B, Thomas R, Middelberg AP. Co-delivery of antigen and a lipophilic anti-inflammatory drug to cells via tailorable nanocarrier emulsion. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;368(1):616–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

