Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase alters microRNA expression and reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 23403951
- PMCID: PMC3622654
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1814
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase alters microRNA expression and reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
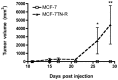
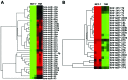
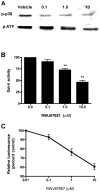
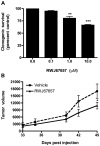
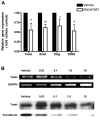
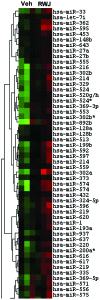
Acquired chemoresistance and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are hallmarks of cancer progression and of increasing clinical relevance. We investigated the role of miRNA and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in the progression of breast cancer to a drug-resistant and mesenchymal phenotype. We demonstrate that acquired death receptor resistance results in increased hormone-independent tumorigenesis compared to hormone-sensitive parental cells. Utilizing global miRNA gene expression profiling, we identified miRNA alterations associated with the development of death receptor resistance and EMT progression. We further investigated the role of p38 MAPK in this process, showing dose-dependent inactivation of p38 by its inhibitor RWJ67657 and decreased downstream ATF and NF‑κB signaling. Pharmacological inhibition of p38 also decreased chemoresistant cancer tumor growth in xenograft animal models. Interestingly, inhibition of p38 partially reversed the EMT changes found in this cell system, as illustrated by decreased gene expression of the EMT markers Twist, Snail, Slug and ZEB and protein and mRNA levels of Twist, a known EMT promoter, concomitant with decreased N‑cadherin protein. RWJ67657 treatment also altered the expression of several miRNAs known to promote therapeutic resistance, including miR‑200, miR‑303, miR‑302, miR‑199 and miR‑328. Taken together, our results demonstrate the roles of multiple microRNAs and p38 signaling in the progression of cancer and demonstrate the therapeutic potential of targeting the p38 MAPK pathway for reversing EMT in an advanced tumor phenotype.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acquired resistance to zoledronic acid and the parallel acquisition of an aggressive phenotype are mediated by p38-MAP kinase activation in prostate cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2013 May 23;4(5):e641. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.165. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23703386 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is associated with rapamycin resistance.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 14;6(23):19500-13. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3669. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25944619 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Platycodon grandiflorus on doxorubicin resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec;55(6):1307-1314. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10271-9. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39316256
-
Roles of p38 MAPKs in invasion and metastasis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):79-84. doi: 10.1042/BST20110676. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260669 Review.
-
miRNAs Modulate the Dichotomy of Cisplatin Resistance or Sensitivity in Breast Cancer: An Update of Therapeutic Implications.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(9):1069-1081. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200903145939. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32885760 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-CD20 antibody induces the improvement of cytokine-induced killer cell activity via the STAT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Apr;9(4):1215-1222. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2264. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 25780412 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNAs in Gene Expression and Signaling Response of Tumor Cells to an Acidic Environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 29;24(23):16919. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316919. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069241 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer-Stromal Interactions: Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cell Age and Cancer Subtype Mediated Remodeling.Stem Cells Dev. 2022 Oct;31(19-20):604-620. doi: 10.1089/scd.2021.0279. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Stem Cells Dev. 2022. PMID: 35579936 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 enhances AML stem cell line KG1a chemosensitivity to daunorubicin by promoting late apoptosis, cell growth arrest in S-phase, and miR-328-3p upregulation.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Jun;32(6):102055. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102055. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38699598 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Subtyping of Serous Ovarian Cancer Based on Multi-omics Data.Sci Rep. 2016 May 17;6:26001. doi: 10.1038/srep26001. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27184229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC. Induction of apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256:42–49. - PubMed
-
- Seidman AD. Chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer: a current perspective. Semin Oncol. 1996;23:55–59. - PubMed
-
- Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell. 1995;81:495–504. - PubMed
-
- Herrnring C, Reimer T, Jeschke U, et al. Expression of the apoptosis-inducing ligands FasL and TRAIL in malignant and benign human breast tumors. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000;113:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Zyad A, Benard J, Tursz T, Clarke R, Chouaib S. Resistance to TNF-alpha and adriamycin in the human breast cancer MCF-7 cell line: relationship to MDR1, MnSOD, and TNF gene expression. Cancer Res. 1994;54:825–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

