Susceptibility of hepatoma-derived cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors is associated with ID2 expression
- PMID: 23403953
- PMCID: PMC3622658
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1811
Susceptibility of hepatoma-derived cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors is associated with ID2 expression
Abstract
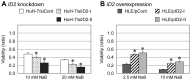
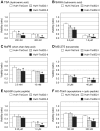
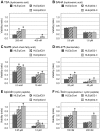
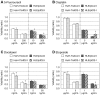
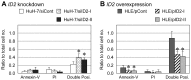
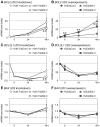
Downregulation of inhibitor of DNA binding 2 (ID2) is associated with poor prognosis in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, to search for effective antitumor drugs for the treatment of HCC exhibiting poor prognostic indicators, we used two HCC-derived cell lines (HuH-7 and HLE) to alter ID2 levels. Specifically, ID2 expression was knocked down in HuH-7 cells via transfection with ID2-specific small interfering RNAs and separately ID2 was overexpressed in HLE cells via an ID2 expression plasmid vector. To assess the effect of antitumor drugs, MTS assay was performed. Annexin V staining was used to evaluate apoptosis and real-time RT-PCR was used to measure mRNA levels. ID2 knockdown cells were more susceptible to histone deacethylase (HDAC) inhibitors including sodium butyrate (NaB), sodium 4-phenyl-butyrate, tricostatin A, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, MS-275, apicidin and HC-toxin. Conversely, cells that overexpressed ID2 were less susceptible than control cells to HDAC inhibitors. NaB-induced apoptosis was inversely correlated with ID2 expression. Expression of the anti-apoptotic mRNA BCL2 was induced by NaB in control cells, but this induction of BCL2 was inhibited by ID2 knockdown and strengthened by ID2 overexpression. Expression of another anti-apoptotic mRNA, BCL2L1, was decreased by NaB administration and then partially recovered. However, in ID2 knockdown cells, BCL2L1 levels did not recover from NaB-induced suppression. ID2 affected the susceptibility of two HCC-derived cell lines to an HDAC inhibitor by regulating the expression of anti-apoptotic genes. Therefore, HDAC inhibitors may be effective for the treatment of HCC for which the prognosis is poor based on ID2 downregulation and ID2 could serve as a marker that is predictive of the clinical response to HDAC inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors radiosensitize human melanoma cells by suppressing DNA repair activity.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 1;11(13):4912-22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2088. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16000590
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors reduce VEGF production and induce growth suppression and apoptosis in human mantle cell lymphoma.Eur J Haematol. 2006 Jan;76(1):42-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2005.00546.x. Eur J Haematol. 2006. PMID: 16343270
-
HDAC inhibitor treatment of hepatoma cells induces both TRAIL-independent apoptosis and restoration of sensitivity to TRAIL.Hepatology. 2006 Mar;43(3):425-34. doi: 10.1002/hep.21054. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16583461
-
Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor MPT0G009 induces cell apoptosis and synergistic anticancer activity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand against human hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):402-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6352. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26587975 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium butyrate-induced DAPK-mediated apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;27(4):1111-5. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1585. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22160140 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic actions of environmental factors and promising drugs for cancer therapy.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):2049-2056. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7597. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434904 Free PMC article.
-
A stem cell medium containing neural stimulating factor induces a pancreatic cancer stem-like cell-enriched population.Int J Oncol. 2014 Nov;45(5):1857-66. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2603. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25118635 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of histone deacetylases in brain tumors.CNS Oncol. 2013 Jul;2(4):359-76. doi: 10.2217/cns.13.24. CNS Oncol. 2013. PMID: 25054580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression and pathway analysis of CTNNB1 in cancer and stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2016 Nov 26;8(11):384-395. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i11.384. World J Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 27928465 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the use of benzoate, phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate ammonia scavengers for interrogating and modifying liver nitrogen metabolism and its implications in urea cycle disorders and liver disease.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017 Apr;13(4):439-448. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2017.1262843. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27860485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;2002;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M, Llovet JM. Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:215–219. - PubMed
-
- Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, Mori N, Tamesa T, Okada T, Takemoto N, Sakamoto K, Hamada K, Ishitsuka H, Miyamoto T, Uchimura S, Hamamoto Y. Self-organizing-map-based molecular signature representing the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:1089–1100. - PubMed
-
- Damdinsuren B, Nagano H, Kondo M, Yamamoto H, Hiraoka N, Yamamoto T, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Umeshita K, Dono K, Nakamori S, Wakasa K, Sakon M, Monden M. Expression of Id proteins in human hepatocellular carcinoma: relevance to tumor dedifferentiation. Int J Oncol. 2005;26:319–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

