Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Surgical technique: Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a technique to aid closed reduction
- PMID: 23404414
- PMCID: PMC3613559
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-012-2764-y
Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Surgical technique: Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a technique to aid closed reduction
Abstract
Background: Anatomic reduction of some displaced pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures is not attainable via closed manipulation, thus necessitating open reduction. Open reduction has been associated with increased complications, including elbow stiffness, scarring, iatrogenic neurovascular injury, and longer hospital stays. Using a Schanz pin to aid in closed reduction may decrease the need for conversion to an open procedure, possibly reducing morbidity.
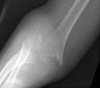
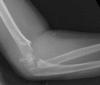
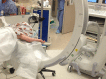
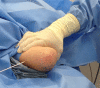
Description of technique: A percutaneously placed 2.5-mm Schanz pin was drilled into the posterior humeral diaphysis and used as a joystick to reduce anterior and posterior, varus and valgus, and rotational deformity. The fracture then was stabilized with 0.62-mm K-wires placed under fluoroscopy and the Schanz pin then was removed.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all displaced pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures treated by one surgeon from March 2002 through December 2010, with 143 fractures meeting criteria for inclusion. These fractures then were divided into two groups. Group 1 (90 fractures) included fractures treated before implantation of the Schanz pin. In this group, if successful reduction could not be achieved via closed manipulations, a formal open reduction was performed. In Group 2, (53 fractures) the Schanz pin technique was used to assist with reduction of fractures that were not reduced successfully by closed manipulations. All fractures were stabilized with the 0.62-mm K-wires after the reductions. To equalize group size, the 37 most remote fractures in Group 1 were removed, leaving a final 53 fractures in each group for analysis. Demographics, injury data, operative technique, complications, and radiographic reduction were analyzed. The minimum followup for both groups was 3.3 weeks (average, 13 weeks; range, 3.3-130 weeks).
Results: Fewer fractures in Group 2 (one of 53, 1.9%) compared with Group 1 (seven of 53, 13%) underwent open reduction. Ten fractures in Group 2 underwent the Schanz pin technique, and none of these had open reductions. We found no difference between the groups concerning fracture alignment at final followup or postoperative complications.
Conclusions: A posteriorly placed Schanz pin aids in anatomic reduction and decreases the need for open treatment of displaced pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures, without compromising the complication rate or final radiographic outcome.
Figures
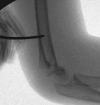
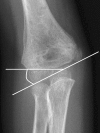
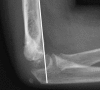
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Surgical technique: Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a technique to aid closed reduction.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jan;472(1):379-80. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3299-6. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24136800 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to the Letter to the Editor: Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Surgical technique: Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: a technique to aid closed reduction.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Jan;472(1):381-2. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3355-2. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24158543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- CPT® 2012 Professional. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association Press; 2011.
-
- Attenborough CG. Remodeling of the humerus after supracondylar fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953;35:386–395. - PubMed
-
- Elstrom JA, Pankovich AM, Kassab MT. Irreducible supracondylar fracture of the humerus: a report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57:680–681. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

