Radiographic findings in revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions from the Mars cohort
- PMID: 23404491
- PMCID: PMC3716860
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1329717
Radiographic findings in revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions from the Mars cohort
Abstract
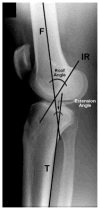
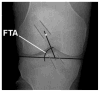
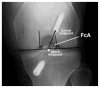
The Multicenter ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) Revision Study (MARS) group was developed to investigate revision ACL reconstruction outcomes. An important part of this is obtaining and reviewing radiographic studies. The goal for this radiographic analysis is to establish radiographic findings for a large revision ACL cohort to allow comparison with future studies. The study was designed as a cohort study. Various established radiographic parameters were measured by three readers. These included sagittal and coronal femoral and tibial tunnel position, joint space narrowing, and leg alignment. Inter- and intraobserver comparisons were performed. Femoral sagittal position demonstrated 42% were more than 40% anterior to the posterior cortex. On the sagittal tibia tunnel position, 49% demonstrated some impingement on full-extension lateral radiographs. Limb alignment averaged 43% medial to the medial edge of the tibial plateau. On the Rosenberg view (45-degree flexion view), the minimum joint space in the medial compartment averaged 106% of the opposite knee, but it ranged down to a minimum of 4.6%. Lateral compartment narrowing at its minimum on the Rosenberg view averaged 91.2% of the opposite knee, but it ranged down to a minimum of 0.0%. On the coronal view, verticality as measured by the angle from the center of the tibial tunnel aperture to the center of the femoral tunnel aperture measured 15.8 degree ± 6.9% from vertical. This study represents the radiographic findings in the largest revision ACL reconstruction series ever assembled. Findings were generally consistent with those previously demonstrated in the literature.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Figures



References
-
- George MS, Dunn WR, Spindler KP. Current concepts review: revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):2026–2037. - PubMed
-
- Kamath GV, Redfern JC, Greis PE, Burks RT. Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39 (1):199–217. - PubMed
-
- Wright RW, Dunn WR, Amendola A, et al. MOON Cohort. Anterior cruciate ligament revision reconstruction: two-year results from the MOON cohort. J Knee Surg. 2007;20(4):308–311. - PubMed
-
- Vergis A, Gillquist J. Graft failure in intra-articular anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions: a review of the literature. Arthroscopy. 1995;11(3):312–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

