Purinergic signaling in inflammatory cells: P2 receptor expression, functional effects, and modulation of inflammatory responses
- PMID: 23404828
- PMCID: PMC3757148
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-013-9357-4
Purinergic signaling in inflammatory cells: P2 receptor expression, functional effects, and modulation of inflammatory responses
Abstract
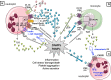
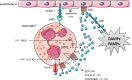
Extracellular ATP and related nucleotides promote a wide range of pathophysiological responses via activation of cell surface purinergic P2 receptors. Almost every cell type expresses P2 receptors and/or exhibit regulated release of ATP. In this review, we focus on the purinergic receptor distribution in inflammatory cells and their implication in diverse immune responses by providing an overview of the current knowledge in the literature related to purinergic signaling in neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils, and mast cells. The pathophysiological role of purinergic signaling in these cells include among others calcium mobilization, actin polymerization, chemotaxis, release of mediators, cell maturation, cytotoxicity, and cell death. We finally discuss the therapeutic potential of P2 receptor subtype selective drugs in inflammatory conditions.
Figures




References
-
- Vitiello L, Gorini S, Rosano G, la Sala A (2012) Immunoregulation through extracellular nucleotides. Blood 120(3):511–518 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

