Obesity and the microvasculature: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23405065
- PMCID: PMC3566162
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052708
Obesity and the microvasculature: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity are thought to significantly influence a person's risk of cardiovascular disease, possibly via its effect on the microvasculature. Retinal vascular caliber is a surrogate marker of microvascular disease and a predictor of cardiovascular events. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to determine the association between body mass index (BMI) and retinal vascular caliber.
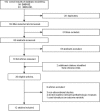
Methods and findings: Relevant studies were identified by searches of the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases from 1966 to August 2011. Standardized forms were used for data extraction. Among over 44,000 individuals, obese subjects had narrower arteriolar and wider venular calibers when compared with normal weight subjects, independent of conventional cardiovascular risk factors. In adults, a 1 kg/m(2) increase in BMI was associated with a difference of 0.07 μm [95% CI: -0.08; -0.06] in arteriolar caliber and 0.22 μm [95% CI: 0.21; 0.23] in venular caliber. Similar results were found for children.
Conclusions: Higher BMI is associated with narrower retinal arteriolar and wider venular calibers. Further prospective studies are needed to examine whether a causative relationship between BMI and retinal microcirculation exists.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Fortunato G, Rubba P, Panico S, Trono D, Tinto N, et al. (2003) A paraoxonase gene polymorphism, PON 1 (55), as an independent risk factor for increased carotid intima-media thickness in middle-aged women. Atherosclerosis 167: 141–148. - PubMed
-
- Kotsis VT, Stabouli SV, Papamichael CM, Zakopoulos NA (2006) Impact of obesity in intima media thickness of carotid arteries. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14: 1708–1715. - PubMed
-
- Berni A, Giuliani A, Tartaglia F, Tromba L, Sgueglia M, et al. (2011) Effect of vascular risk factors on increase in carotid and femoral intima-media thickness. Identification of a risk scale. Atherosclerosis 216: 109–114. - PubMed
-
- Czernichow S, Greenfield JR, Galan P, Bastard JP, Charnaux N, et al. (2010) Microvascular dysfunction in healthy insulin-sensitive overweight individuals. J Hypertens 28: 325–332. - PubMed
-
- Czernichow S, Greenfield JR, Galan P, Jellouli F, Safar ME, et al. (2010) Macrovascular and microvascular dysfunction in the metabolic syndrome. Hypertens Res 33: 293–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

