Binding of the radioligand SIL23 to α-synuclein fibrils in Parkinson disease brain tissue establishes feasibility and screening approaches for developing a Parkinson disease imaging agent
- PMID: 23405108
- PMCID: PMC3566091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055031
Binding of the radioligand SIL23 to α-synuclein fibrils in Parkinson disease brain tissue establishes feasibility and screening approaches for developing a Parkinson disease imaging agent
Abstract
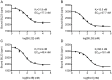
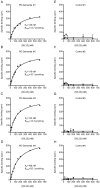
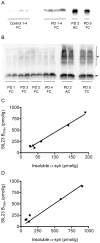
Accumulation of α-synuclein (α-syn) fibrils in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites is the pathological hallmark of Parkinson disease (PD). Ligands that bind α-syn fibrils could be utilized as imaging agents to improve the diagnosis of PD and to monitor disease progression. However, ligands for α-syn fibrils in PD brain tissue have not been previously identified and the feasibility of quantifying α-syn fibrils in brain tissue is unknown. We report the identification of the (125)I-labeled α-syn radioligand SIL23. [(125)I]SIL23 binds α-syn fibrils in postmortem brain tissue from PD patients as well as an α-syn transgenic mouse model for PD. The density of SIL23 binding sites correlates with the level of fibrillar α-syn in PD brain tissue, and [(125)I]SIL23 binding site densities in brain tissue are sufficiently high to enable in vivo imaging with high affinity ligands. These results identify a SIL23 binding site on α-syn fibrils that is a feasible target for development of an α-syn imaging agent. The affinity of SIL23 for α-syn and its selectivity for α-syn versus Aβ and tau fibrils is not optimal for imaging fibrillar α-syn in vivo, but we show that SIL23 competitive binding assays can be used to screen additional ligands for suitable affinity and selectivity, which will accelerate the development of an α-syn imaging agent for PD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
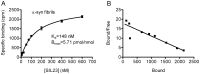
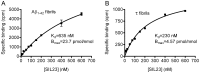

References
-
- Hely MA, Reid WG, Adena MA, Halliday GM, Morris JG (2008) The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord 23: 837–844. - PubMed
-
- Hurtig HI, Trojanowski JQ, Galvin J, Ewbank D, Schmidt ML, et al. (2000) Alpha-synuclein cortical Lewy bodies correlate with dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54: 1916–1921. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318: 121–134. - PubMed
-
- Clayton DF, George JM (1998) The synucleins: a family of proteins involved in synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease. Trends Neurosci 21: 249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 NS061025/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS075321/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH092797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS058714/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH092797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS075527/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075321/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS061025/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041509/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS41509/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH092797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058714/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS075321/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075527/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS090214/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

