TGF-β and TGF-β/Smad signaling in the interactions between Echinococcus multilocularis and its hosts
- PMID: 23405141
- PMCID: PMC3566151
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055379
TGF-β and TGF-β/Smad signaling in the interactions between Echinococcus multilocularis and its hosts
Abstract
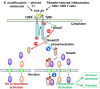
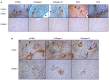
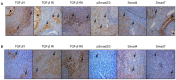
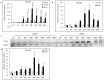
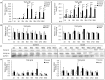
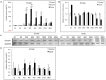
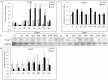
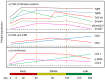
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is characterized by the development of irreversible fibrosis and of immune tolerance towards Echinococcus multilocularis (E. multilocularis). Very little is known on the presence of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and other components of TGF-β/Smad pathway in the liver, and on their possible influence on fibrosis, over the various stages of infection. Using Western Blot, qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry, we measured the levels of TGF-β1, TGF-β receptors, and down-stream Smads activation, as well as fibrosis marker expression in both a murine AE model from day 2 to 360 post-infection (p.i.) and in AE patients. TGF-β1, its receptors, and down-stream Smads were markedly expressed in the periparasitic infiltrate and also in the hepatocytes, close to and distant from AE lesions. Fibrosis was significant at 180 days p.i. in the periparasitic infiltrate and was also present in the liver parenchyma, even distant from the lesions. Over the time course after infection TGF-β1 expression was correlated with CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio long described as a hallmark of AE severity. The time course of the various actors of the TGF-β/Smad system in the in vivo mouse model as well as down-regulation of Smad7 in liver areas close to the lesions in human cases highly suggest that TGF-β plays an important role in AE both in immune tolerance against the parasite and in liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The expression dynamics of transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling in the liver fibrosis experimentally caused by Clonorchis sinensis.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Feb 4;8:70. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0675-y. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 25649869 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway regulates Th17/Treg balance during Echinococcus multilocularis infection.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 May;20(1):248-57. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.038. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24631515
-
HuangQi Decoction Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis via TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(5):1761-74. doi: 10.1159/000443115. Epub 2016 May 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27161221
-
Molecular survival strategies of Echinococcus multilocularis in the murine host.Parasitol Int. 2006;55 Suppl:S45-9. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.006. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Parasitol Int. 2006. PMID: 16352460 Review.
-
Diverse roles of TGF-β/Smads in renal fibrosis and inflammation.Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(7):1056-67. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.1056. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21927575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kupffer Cells: Important Participant of Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 29;10:8. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00008. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32064239 Free PMC article.
-
The expression dynamics of transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling in the liver fibrosis experimentally caused by Clonorchis sinensis.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Feb 4;8:70. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0675-y. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 25649869 Free PMC article.
-
CD3/TCRE Expression and Immunoregulatory Milieu Induced in a Secondary Intermediate Host by Different Phases of Hydatid Cyst.Acta Parasitol. 2021 Dec;66(4):1490-1498. doi: 10.1007/s11686-021-00408-1. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Acta Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34110592
-
Structural changes and expression of hepatic fibrosis-related proteins in coculture of Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces and human hepatic stellate cells.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Dec 2;14(1):593. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-05037-1. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34857049 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of subarachnoid cysts of Taenia solium reveals mechanisms for uncontrolled proliferation and adaptations to the microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2024 May 23;14(1):11833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61973-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38782926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vuitton DA, Zhou H, Bresson-Hadni S, Wang Q, Piarroux M, et al. (2003) Epidemiology of alveolar echinococcosis with particular reference to China and Europe. Parasitology 127 Suppl: S87–107 - PubMed
-
- Vuitton DA, Zhang SL, Yang Y, Godot V, Beurton I, et al. (2006) Survival strategy of Echinococcus multilocularis in the human host. Parasitol Int 55 Suppl: S51–55 - PubMed
-
- Grenard P, Bresson-Hadni S, El Alaoui S, Chevallier M, Vuitton DA, et al. (2001) Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking is involved in the stabilization of extracellular matrix in human liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 35: 367–375. - PubMed
-
- Guerret S, Vuitton DA, Liance M, Pater C, Carbillet JP (1998) Echinococcus multilocularis: relationship between susceptibility/resistance and liver fibrogenesis in experimental mice. Parasitol Res 84: 657–667. - PubMed
-
- Ricard-Blum S, Bresson-Hadni S, Guerret S, Grenard P, Volle PJ, et al. (1996) Mechanism of collagen network stabilization in human irreversible granulomatous liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 111: 172–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

