De novo synthesized estradiol protects against methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat hippocampal slices
- PMID: 23405170
- PMCID: PMC3566000
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055559
De novo synthesized estradiol protects against methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat hippocampal slices
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(4). doi:10.1371/annotation/52376e1c-1a2d-44af-a129-849345da78a0
Abstract
Background: Estrogen, a class of female sex steroids, is neuroprotective. Estrogen is synthesized in specific areas of the brain. There is a possibility that the de novo synthesized estrogen exerts protective effect in brain, although direct evidence for the neuroprotective function of brain-synthesized estrogen has not been clearly demonstrated. Methylmercury (MeHg) is a neurotoxin that induces neuronal degeneration in the central nervous system. The neurotoxicity of MeHg is region-specific, and the molecular mechanisms for the selective neurotoxicity are not well defined. In this study, the protective effect of de novo synthesized 17β-estradiol on MeHg-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampus was examined.
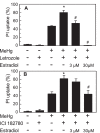
Methodology/principal findings: Neurotoxic effect of MeHg on hippocampal organotypic slice culture was quantified by propidium iodide fluorescence imaging. Twenty-four-hour treatment of the slices with MeHg caused cell death in a dose-dependent manner. The toxicity of MeHg was attenuated by pre-treatment with exogenously added estradiol. The slices de novo synthesized estradiol. The estradiol synthesis was not affected by treatment with 1 µM MeHg. The toxicity of MeHg was enhanced by inhibition of de novo estradiol synthesis, and the enhancement of toxicity was recovered by the addition of exogenous estradiol. The neuroprotective effect of estradiol was inhibited by an estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist, and mimicked by pre-treatment of the slices with agonists for ERα and ERβ, indicating the neuroprotective effect was mediated by ERs.
Conclusions/significance: Hippocampus de novo synthesized estradiol protected hippocampal cells from MeHg-induced neurotoxicity via ERα- and ERβ-mediated pathways. The self-protective function of de novo synthesized estradiol might be one of the possible mechanisms for the selective sensitivity of the brain to MeHg toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Progesterone inhibits estrogen-mediated neuroprotection against excitotoxicity by down-regulating estrogen receptor-β.J Neurochem. 2010 Dec;115(5):1277-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07038.x. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20977477 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective role of estradiol against neuronal death induced by glucose deprivation in cultured rat hippocampal neurons.Neuroendocrinology. 2012;96(1):41-50. doi: 10.1159/000334229. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Neuroendocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22213775
-
Estrogen receptor alpha and beta differentially regulate intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics leading to ERK phosphorylation and estrogen neuroprotection in hippocampal neurons.Brain Res. 2007 Oct 3;1172:48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.092. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17803971
-
Estrogens are neuroprotective factors for hypertensive encephalopathy.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Feb;146:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24736028 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the memory-enhancing effects of estradiol.Horm Behav. 2015 Aug;74:4-18. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 8. Horm Behav. 2015. PMID: 25960081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase-Mediated Genotoxicity of 2-Methoxyestradiol in Hippocampal HT22 Cell Line.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Sep;53(7):5030-40. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9434-5. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26381428
-
Chronic exposure to methylmercury enhances the anorexigenic effects of leptin in C57BL/6J male mice.Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Jan;147:111924. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111924. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33338554 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived estrogen and neural function.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:793-817. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.014. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34823913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-dependent and non-monotonic enhancement and unmasking of methylmercury neurotoxicity by prenatal stress.Neurotoxicology. 2014 Mar;41:123-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Neurotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 24502960 Free PMC article.
-
Intriguing roles of hippocampus-synthesized 17β-estradiol in the modulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity.J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54(2):271-81. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0285-8. Epub 2014 Apr 15. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24729128 Review.
References
-
- McEwen B (2002) Estrogen actions throughout the brain. Recent Prog Horm Res 57: 357–384. - PubMed
-
- Bourque M, Dluzen DE, Di Paolo T (2009) Neuroprotective actions of sex steroids in Parkinson's disease. Front Neuroendocrinol 30: 142–157. - PubMed
-
- Behl C (2002) Oestrogen as a neuroprotective hormone. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 433–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

