Th9 cells: differentiation and disease
- PMID: 23405898
- PMCID: PMC3982928
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12028
Th9 cells: differentiation and disease
Abstract
CD4(+) T-helper cells regulate immunity and inflammation through the acquisition of potential to secrete specific cytokines. The acquisition of cytokine-secreting potential, in a process termed T-helper cell differentiation, is a response to multiple environmental signals including the cytokine milieu. The most recently defined subset of T-helper cells are termed Th9 and are identified by the potent production of interleukin-9 (IL-9). Given the pleiotropic functions of IL-9, Th9 cells might be involved in pathogen immunity and immune-mediated disease. In this review, I focus on recent developments in understanding the signals that promote Th9 differentiation, the transcription factors that regulate IL-9 expression, and finally the potential roles for Th9 cells in immunity in vivo.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
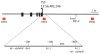
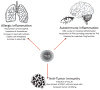
References
-
- Staudt V, et al. Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity. 2010;33:192–202. - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1341–1346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

