Antimalarial drug artemisinin extenuates amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 23406388
- PMCID: PMC6493386
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12066
Antimalarial drug artemisinin extenuates amyloidogenesis and neuroinflammation in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
Background: The activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in neuroinflammation, which is closely linked to Alzheimer's disease (AD). In vivo and in vitro studies have suggested that artemisinin shows antiinflammatory effects in inflammation-related diseases. However, the impacts of artemisinin on AD have not been investigated.
Aims: In this study, 5-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice were treated daily with 40 mg/kg artemisinin for 30 days by intraperitoneal injection to evaluate the effects of artemisinin on AD.
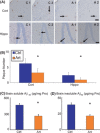
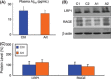
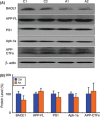
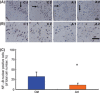
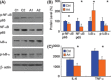
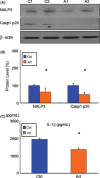
Results: We found that artemisinin treatment (1) decreased neuritic plaque burden; (2) did not alter Aβ transport across the blood-brain barrier; (3) regulated APP processing via inhibiting β-secretase activity; (4) inhibited NF-κB activity and NALP3 inflammasome activation in APPswe/PS1dE9 double transgenic mice.
Conclusions: The in vivo study clearly demonstrates that artemisinin has protective effects on AD pathology due to its effects on suppressing NF-κB activity and NALP3 inflammasome activation. Our study suggests that targeting NF-κB activity and NALP3 inflammasome activation offers a valuable intervention for AD.
© 2013 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cummings JL, Cole G. Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2002;287:2335–2338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

