Novel triaryl sulfonamide derivatives as selective cannabinoid receptor 2 inverse agonists and osteoclast inhibitors: discovery, optimization, and biological evaluation
- PMID: 23406429
- PMCID: PMC3967766
- DOI: 10.1021/jm3017464
Novel triaryl sulfonamide derivatives as selective cannabinoid receptor 2 inverse agonists and osteoclast inhibitors: discovery, optimization, and biological evaluation
Abstract
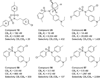
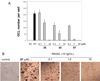
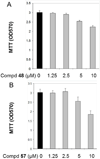
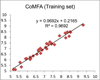
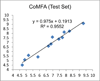
Cannabinoid receptors have gained increasing attention as drug targets for developing potential therapeutic ligands. Here, we report the discovery and optimization of triaryl sulfonamides as a novel series possessing significant CB2 receptor affinity and selectivity. Four sets of triaryl ligands were designed and synthesized for further structural modifications and led to the identification of eight compounds as potent and selective CB2 inverse agonists with high binding affinity (CB2K(i) < 10 nM). Especially, compound 57 exhibited the strongest binding affinity on the CB2 receptor (CB2K(i) of 0.5 nM) and the best selectivity over the CB1 receptor (selectivity index of 2594). Importantly, 57 also showed potent inhibitory activity on osteoclast formation, and it was confirmed by a cell viability assay that the inhibition effects were not derived from the cytotoxicity. Finally, 3D QSAR studies confirmed our SAR findings that three bulky groups play an important role for CB2 receptor binding affinity.
Figures


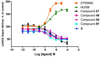

References
-
- Devane WA, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, Stevenson LA, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992;258:1946–1949. - PubMed
-
- Mechoulam R, Ben-Shabat S, Hanus L, Ligumsky M, Kaminski NE, Schatz AR, Gopher A, Almog S, Martin BR, Compton DR, et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995;50:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Sugiura T, Kondo S, Sukagawa A, Nakane S, Shinoda A, Itoh K, Yamashita A, Waku K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: a possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995;215:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Bayewitch M, Rhee MH, Avidor-Reiss T, Breuer A, Mechoulam R, Vogel Z. (−)-Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol antagonizes the peripheral cannabinoid receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:9902–9905. - PubMed
-
- Felder CC, Joyce KE, Briley EM, Mansouri J, Mackie K, Blond O, Lai Y, Ma AL, Mitchell RL. Comparison of the pharmacology and signal transduction of the human cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995;48:443–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

