Treatment of dysferlinopathy with deflazacort: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 23406536
- PMCID: PMC3617000
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-26
Treatment of dysferlinopathy with deflazacort: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Dysferlinopathies are autosomal recessive disorders caused by mutations in the dysferlin (DYSF) gene encoding the dysferlin protein. DYSF mutations lead to a wide range of muscular phenotypes, with the most prominent being Miyoshi myopathy (MM) and limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B (LGMD2B).
Methods: We assessed the one-year-natural course of dysferlinopathy, and the safety and efficacy of deflazacort treatment in a double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. After one year of natural course without intervention, 25 patients with genetically defined dysferlinopathy were randomized to receive deflazacort and placebo for six months each (1 mg/kg/day in month one, 1 mg/kg every 2nd day during months two to six) in one of two treatment sequences.
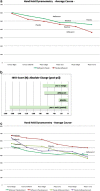
Results: During one year of natural course, muscle strength declined about 2% as measured by CIDD (Clinical Investigation of Duchenne Dystrophy) score, and 76 Newton as measured by hand-held dynamometry. Deflazacort did not improve muscle strength. In contrast, there is a trend of worsening muscle strength under deflazacort treatment, which recovers after discontinuation of the study drug. During deflazacort treatment, patients showed a broad spectrum of steroid side effects.
Conclusion: Deflazacort is not an effective therapy for dysferlinopathies, and off-label use is not warranted. This is an important finding, since steroid treatment should not be administered in patients with dysferlinopathy, who may be often misdiagnosed as polymyositis.
Trial registration: This clinical trial was registered at http://www.ClincalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT00527228, and was always freely accessible to the public.
Figures



References
-
- Bashir R, Britton S, Strachan T, Keers S, Vafiadaki E, Lako M, Richard I, Marchand S, Bourg N, Argov Z, Sadeh M, Mahjneh I, Marconi G, Passos-Bueno MR, Moreira Ede S, Zatz M, Beckmann JS, Bushby K. A gene related to Caenorhabditis elegans spermatogenesis factor fer-1 is mutated in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B. Nat Genet. 1998;20:37–42. doi: 10.1038/1689. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Aoki M, Illa I, Wu C, Fardeau M, Angelini C, Serrano C, Urtizberea JA, Hentati F, Hamida MB, Bohlega S, Culper EJ, Amato AA, Bossie K, Oeltjen J, Bejaoui K, McKenna-Yasek D, Hosler BA, Schurr E, Arahata K, de Jong PJ, Brown RH Jr. Dysferlin, a novel skeletal muscle gene, is mutated in Miyoshi myopathy and limb girdle muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1998;20:31–36. doi: 10.1038/1682. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moore SA, Shilling CJ, Westra S, Wall C, Wicklund MP, Stolle C, Brown CA, Michele DE, Piccolo F, Winder TL, Stence A, Barresi R, King N, King W, Florence J, Campbell KP, Fenichel GM, Stedman HH, Kissel JT, Griggs RC, Pandya S, Mathews KD, Pestronk A, Serrano C, Darvish D, Mendell JR. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy in the United States. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:995–1003. doi: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000235854.77716.6c. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi K, Saijo K, Kuryu Y. Four cases of distal myopathy in two families. Jpn J Hum Genet. 1967;12:113.
-
- Illa I, Serrano-Munuera C, Gallardo E, Lasa A, Rojas-Garcia R, Palmer J, Gallano P, Baiget M, Matsuda C, Brown RH. Distal anterior compartment myopathy: a dysferlin mutation causing a new muscular dystrophy phenotype. Ann Neurol. 2001;49:130–134. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(200101)49:1<130::AID-ANA22>3.0.CO;2-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

