Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 23406779
- PMCID: PMC3711981
- DOI: 10.4161/viru.23753
Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
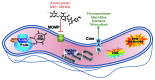
Campylobacter jejuni is a major cause of food-borne gastroenteritis worldwide. While mortality is low, morbidity imparted by post-infectious sequelae such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, Reiter syndrome/reactive arthritis and irritable bowel syndrome is significant. In addition, the economic cost is high due to lost productivity. Food animals, particularly poultry, are the main reservoirs of C. jejuni. The over-use of antibiotics in the human population and in animal husbandry has led to an increase in antibiotic-resistant infections, particularly with fluoroquinolones. This is problematic because C. jejuni gastroenteritis is clinically indistinguishable from that caused by other bacterial pathogens, and such illnesses are usually treated empirically with fluoroquinolones. Since C. jejuni is naturally transformable, acquisition of additional genes imparting antibiotic resistance is likely. Therefore, an understanding of the antibiotic resistance mechanisms in C. jejuni is needed to provide proper therapy both to the veterinary and human populations.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; CmeABC; MOMP; antibiotic resistance; efflux pump; major outer membrane protein; porin.
Figures
References
-
- Eurosurveillance editorial team The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2010. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:20113. - PubMed
-
- EFSA The Community Summary Report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from animals and food in the European Union in 2008. Eur Food Safety Auth J. 2010;8:1658–919.
-
- OzFoodNet Working Group Monitoring the incidence and causes of diseases potentially transmitted by food in Australia: annual report of the OzFoodNet Network, 2009. Commun Dis Intell. 2010;34:396–426. - PubMed
-
- Notifiable and Other Diseases in New Zealand. Annula Report 2011. In: The Institute of Environmental Science and Research Ltd. Porirua, New Zealand; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
