Cofilin and Vangl2 cooperate in the initiation of planar cell polarity in the mouse embryo
- PMID: 23406901
- PMCID: PMC3585660
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.085316
Cofilin and Vangl2 cooperate in the initiation of planar cell polarity in the mouse embryo
Abstract
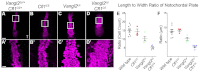
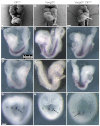
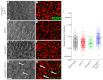
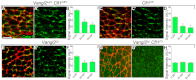
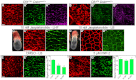
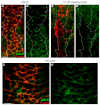
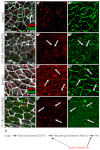
The planar cell polarity (PCP; non-canonical Wnt) pathway is required to orient the cells within the plane of an epithelium. Here, we show that cofilin 1 (Cfl1), an actin-severing protein, and Vangl2, a core PCP protein, cooperate to control PCP in the early mouse embryo. Two aspects of planar polarity can be analyzed quantitatively at cellular resolution in the mouse embryo: convergent extension of the axial midline; and posterior positioning of cilia on cells of the node. Analysis of the spatial distribution of brachyury(+) midline cells shows that the Cfl1 mutant midline is normal, whereas Vangl2 mutants have a slightly wider midline. By contrast, midline convergent extension fails completely in Vangl2 Cfl1 double mutants. Planar polarity is required for the posterior positioning of cilia on cells in the mouse node, which is essential for the initiation of left-right asymmetry. Node cilia are correctly positioned in Cfl1 and Vangl2 single mutants, but cilia remain in the center of the cell in Vangl2 Cfl1 double mutants, leading to randomization of left-right asymmetry. In both the midline and node, the defect in planar polarity in the double mutants arises because PCP protein complexes fail to traffic to the apical cell membrane, although other aspects of apical-basal polarity are unaffected. Genetic and pharmacological experiments demonstrate that F-actin remodeling is essential for the initiation, but not maintenance, of PCP. We propose that Vangl2 and cofilin cooperate to target Rab11(+) vesicles containing PCP proteins to the apical membrane during the initiation of planar cell polarity.
Figures

References
-
- Bastock R., Strutt H., Strutt D. (2003). Strabismus is asymmetrically localised and binds to Prickle and Dishevelled during Drosophila planar polarity patterning. Development 130, 3007–3014 - PubMed
-
- Bellomo D., Lander A., Harragan I., Brown N. A. (1996). Cell proliferation in mammalian gastrulation: the ventral node and notochord are relatively quiescent. Dev. Dyn. 205, 471–485 - PubMed
-
- Blair A., Tomlinson A., Pham H., Gunsalus K. C., Goldberg M. L., Laski F. A. (2006). Twinstar, the Drosophila homolog of cofilin/ADF, is required for planar cell polarity patterning. Development 133, 1789–1797 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

