Joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: assessment of a new scoring method
- PMID: 23406946
- PMCID: PMC3672701
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4163
Joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: assessment of a new scoring method
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to assess a novel approach for the quantification of finger joint space narrowing and joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) focusing on the peripheral hand articulations.
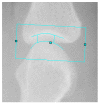
Methods: A total of 280 patients with verified RA underwent computerized semi-automated measurements of joint space distance at the finger articulations based on radiographs. The Z-Score, which can differentiate between joint space alterations caused by RA versus age/gender-related changes, was calculated as a comparative parameter. The severity of joint space narrowing was also quantified by the Sharp Score. Sensitivity and specificity of the Z-Score (based on joint space widths differentiated for each peripheral finger joint) were evaluated to reveal the potential for the occurrence of erosions. Additionally, the potential of the Z-Score regarding the differentiation of therapeutic effects on joint space widths in patients under a therapy of methotrexate versus leflunomide was performed.
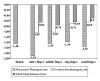
Results: The Z-Scores of finger articulations in patients with RA were generally decreased. Metacarpal-phalangeal (MCP) joint articulations showed a continuous significant decline of -1.65±0.30 standard deviations dependent on the Sharp Score. The proximal-interphalangeal joints also revealed a significant reduction of the Z-Score (-0.96±0.31 standard deviations). The sensitivity and specificity of MCP joint space distance for the detection of erosions were 85.4% versus 55.2%. The Sharp Score for joint space narrowing was not able to detect different treatments, whereas an accentuated stabilization of joint space narrowing could be identified for the Z-Score of the MCP joints in patients treated with leflunomide and methotrexate.
Conclusion: The Z-Scoring method based on computer-aided analysis of joint space widths was able to reliably quantify severity-dependent joint space narrowing in RA patients. In the future, calculation of a Z-Score based on gender-specific and age-specific reference data shows the potential for a surrogate marker of RA progression that comprehends the early identification of patients with RA, and in particular those with erosive course of the disease, enabling a timely therapeutic strategy for cartilage protection.
Figures
References
-
- Bridges SL Jr, Causey ZL, Burgos PI, Huynh BQ, Hughes LB, Danila MI, van Everdingen A, Ledbetter S, Conn Dl, Tambane A, Westfall AO, Jonas BL, Callahan LF, Smith ES, Brasington R, Moreland LW, Alarcón GS, van der Heijde D. Radiographic severity of rheumatoid arthritis in African Americans: results from a multicenter observational study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:624–631. doi: 10.1002/acr.20040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lukas C, Sharp JT, Angwin J, Boers M, Duryea J, Hall JR, Kaufman JA, Landewé R, Langs G, Lukas C, Maillefert JF, Bernelot Moens HJ, Peloschek P, Strand V, van der Heijde D. Automated measurement of joint space width in small joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:1288–1293. - PubMed
-
- Böttcher J, Pfeil A, Rosholm A, Petrovitch A, Seidl BE, Malich A, Schäfer ML, Kramer A, Mentzel HJ, Lehmann G, Hein G, Kaiser WA. Digital X-ray radiogrammetry combined with semi-automated analysis of joint space distances as a new diagnostic approach in rheumatoid arthritis - a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3850–3859. doi: 10.1002/art.21606. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharp JT, Angwin J, Boers M, Duryea J, von Ingersleben G, Hall JR, Kauffman JA, Landewé R, Langs G, Lukas C, Maillefert JF, Bernelot Moens HJ, Peloschek P, Strand V, van der Heijde D. Computer based methods for measurement of joint space width: update of an ongoing OMERACT project. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:874–883. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

