FKBP5 and attention bias for threat: associations with hippocampal function and shape
- PMID: 23407841
- PMCID: PMC3732315
- DOI: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.210
FKBP5 and attention bias for threat: associations with hippocampal function and shape
Abstract
Importance: The FKBP5 gene product regulates glucocorticoid receptor (GR) sensitivity and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and has been associated with many stress-related psychiatric disorders. The study of intermediate phenotypes, such as emotion-processing biases and their neural substrates, provides a way to clarify the mechanisms by which FKBP5 dysregulation mediates risk for psychiatric disorders.
Objective: To examine whether allelic variations for a putatively functional single-nucleotide polymorphism associated with FKBP5 gene regulation (rs1360780) would relate differentially to attention bias for threat. this was measured through behavioral response on a dot probe task and hippocampal activation during task performance. Morphologic substrates of differential hippocampal response were also measured.
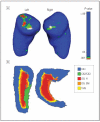
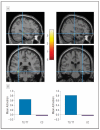
Design: Cross-sectional study conducted from 2010 to 2012 examining associations between genotype, behavioral response, and neural response (using functional magnetic resonance imaging [fMRI]) on the dot probe; voxel-based morphometry and global and local shape analyses were used to measure structural differences in hippocampi between genotype groups.
Setting: Participants were recruited from primary care clinics of a publicly funded hospital in Atlanta, Georgia.
Participants: An African American cohort of adults (N = 103) was separated into 2 groups by genotype: one genotype group included carriers of the rs1360780 T allele, which has been associated with increased risk for posttraumatic stress disorder and affective disorders; the other group did not carry this allele. Behavioral data included both sexes (N = 103); the MRI cohort (n = 36) included only women.
Main outcome measures: Behavioral and fMRI (blood oxygen level-dependent) response, voxel-based morphometry, and shape analyses.
Results: Carriers of the rs1360780 T allele showed an attention bias toward threat compared with individuals without this allele (F1,90 = 5.19, P = .02). Carriers of this allele demonstrated corresponding increases in hippocampal activation and differences in morphology; global and local shape analyses revealed alterations in hippocampal shape for TT/TC compared with CC genotype groups.
Conclusion: Genetic variants of FKBP5 may be associated with risk for stress-related psychiatric disorders via differential effects on hippocampal structure and function, resulting in altered attention response to perceived threat.
Figures

References
-
- Denny WB, Valentine DL, Reynolds PD, Smith DF, Scammell JG. Squirrel monkey immunophilin FKBP51 is a potent inhibitor of glucocorticoid receptor binding. Endocrinology. 2000;141(11):4107–4113. - PubMed
-
- Binder EB, Bradley RG, Liu W, Epstein MP, Deveau TC, Mercer KB, Tang Y, Gillespie CF, Heim CM, Nemeroff CB, Schwartz AC, Cubells JF, Ressler KJ. Association of FKBP5 polymorphisms and childhood abuse with risk of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in adults. JAMA. 2008;299(11):1291–1305. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

