Antenatal betamethasone has a sex-dependent effect on the in vivo response to endothelin in adult sheep
- PMID: 23408033
- PMCID: PMC3627955
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00579.2012
Antenatal betamethasone has a sex-dependent effect on the in vivo response to endothelin in adult sheep
Abstract
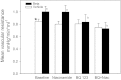
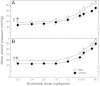
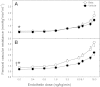
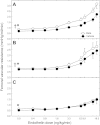
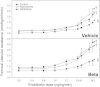
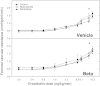
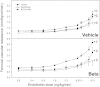
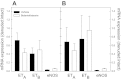
Antenatal steroid administration is associated with multiple cardiometabolic alterations, including hypertension; however, the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are unclear. The aim of the present study was to ascertain, in vivo, the contribution of the endothelin system to the development of hypertension in the adult offspring and the signaling pathway involved. Pregnant sheep were treated with two doses of betamethasone (n = 23) or vehicle (n = 22) at 80 days (~0.55) gestation and allowed to deliver at term. Adult sheep were chronically instrumented under general anesthesia to place vascular catheters and a femoral artery flow probe. Blood pressure and flow were recorded continuously, and femoral artery vascular resistance was calculated before and during administration of endothelin 1 (ET-1). Selective blockers (dantrolene, BQ123, niacinamide) or saline were administered simultaneously. Betamethasone-exposed animals exhibited a significant elevation in mean blood pressure (female: 98 ± 1.8 vs. 92 ± 2.1; males: 97 ± 3.4 vs. 90 ± 2.3; mmHg; P < 0.05). ET-1 elicited a significant increase in blood pressure (F = 56.4; P < 0.001) and in vascular resistance (F = 44.3; P < 0.001) in all groups. A betamethasone effect in the vascular resistance response to ET-1 (F = 25.7; P < 0.001) was present in females only, and the effect was partially blunted by niacinamide (F = 6.6; P < 0.01). Combined administration of niacinamide and BQ123, as well as of dantrolene abolished the betamethasone effect on vascular resistance. No significant differences in mRNA expression of ET(A) or ET(B) in endothelial or smooth muscle cells of resistance-size arteries were observed. We conclude that the betamethasone effect on vascular resistance is mediated by an enhanced response to ET-1 through ET(A) receptor via the cyclic ADPR/ryanodine pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antenatal betamethasone increases vascular reactivity to endothelin-1 by upregulation of CD38/cADPR signaling.J Dev Orig Health Dis. 2014 Feb;5(1):56-62. doi: 10.1017/S2040174413000512. J Dev Orig Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 24847691 Free PMC article.
-
Antenatal betamethasone administration has a dual effect on adult sheep vascular reactivity.Pediatr Res. 2006 Dec;60(6):705-10. doi: 10.1203/01.pdr.0000246481.05231.17. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Pediatr Res. 2006. PMID: 17065564
-
Developmental effect of antenatal exposure to betamethasone on renal angiotensin II activity in the young adult sheep.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Apr;298(4):F847-56. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00497.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20071463 Free PMC article.
-
Betamethasone attenuates oxidant stress in endothelial cells from fetal lambs with persistent pulmonary hypertension.Pediatr Res. 2008 Jan;63(1):67-72. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31815b43ee. Pediatr Res. 2008. PMID: 18043518
-
Differential effects of clinical doses of antenatal betamethasone on nephron endowment and glomerular filtration rate in adult sheep.Reprod Sci. 2010 Feb;17(2):186-95. doi: 10.1177/1933719109351098. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Reprod Sci. 2010. PMID: 19897787 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antenatal Programming of Hypertension: Paradigms, Paradoxes, and How We Move Forward.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022 Dec;24(12):655-667. doi: 10.1007/s11906-022-01227-z. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022. PMID: 36227517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the endothelin system in sexual dimorphism in cardiovascular and renal diseases.Life Sci. 2016 Aug 15;159:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.093. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26939577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in major depression and comorbidity of cardiometabolic disorders: impact of prenatal stress and immune exposures.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jan;44(1):59-70. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0146-1. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30030541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programming of Vascular Dysfunction by Maternal Stress: Immune System Implications.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 10;13:787617. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.787617. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35360231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal metyrapone treatment modulates neonatal cerebrovascular structure, function, and vulnerability to mild hypoxic-ischemic injury.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):R1-R16. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00145.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31577477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adair L, Dahly D. Developmental determinants of blood pressure in adults. Annu Rev Nutr 25: 407–434, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Barone F, Genazzani AA, Conti A, Churchill GC, Palombi F, Ziparo E, Sorrentino V, Galione A, Filippini A. A pivotal role for cADPR-mediated Ca2+ signaling: regulation of endothelin-induced contraction in peritubular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J 16: 697–705, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bielefeldt K, Sharma RV, Whiteis C, Yedidag E, Abboud FM. Tacrolimus (FK506) modulates calcium release and contractility of intestinal smooth muscle. Cell Calcium 22: 507–514, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Cardillo C, Kilcoyne CM, Waclawiw M, Cannon RO, III, Panza JA. Role of endothelin in the increased vascular tone of patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 33: 753–758, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Dalziel SR, Walker NK, Parag V, Mantell C, Rea HH, Rodgers A, Harding JE. Cardiovascular risk factors after antenatal exposure to betamethasone: 30-year follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 365: 1856–1862, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

