Suppression of Gq Function Using Intra-Pipette Delivery of shRNA during Extracellular Recording in the Ventral Tegmental Area
- PMID: 23408114
- PMCID: PMC3569574
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00007
Suppression of Gq Function Using Intra-Pipette Delivery of shRNA during Extracellular Recording in the Ventral Tegmental Area
Abstract
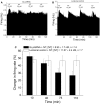
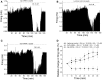
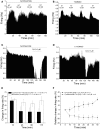
Selective suppression of protein function in the brain can be achieved using specific silencing RNAs administered in vivo. A viral delivery system is often employed to transfect neurons with small hairpin RNA (shRNA) directed against specific proteins, and intervals of several days are allowed between microinjection of the shRNA-containing virus into the brain and experiments to assess suppression of gene function. Here we report studies using extracellular recording of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area (DA VTA neurons) recorded in brain slices in which lentivirus containing shRNA directed against Gq was included in the recording pipette, and suppression of Gq-related function was observed within the time frame of the recording. The action of neurotensin (NT) is associated with activation of Gq, and the firing rate of DA VTA neurons is increased by NT. With shRNA directed against Gq in the pipette, there was a significant reduction of NT excitation within 2 h. Likewise, time-dependent dopamine desensitization, which we have hypothesized to be Gq-dependent, was not observed when shRNA directed against Gq was present in the pipette and dopamine was tested 2 h after initiation of recording. As the time interval (2 h) is relatively short, we tested whether blockade of protein synthesis with cycloheximide delivered via the recording pipette would alter Gq-linked responses similarly. Both NT-induced excitation and dopamine desensitization were inhibited in the presence of cycloheximide. Inclusion of shRNA in the recording pipette may be an efficient and selective way to dampen responses linked to Gq, and, more generally, the use of lentiviral-packaged shRNA in the recording pipette is a means to produce selective inhibition of the function of specific proteins in experiments.
Keywords: Gq; desensitization; dopamine D2 receptor; lentivirus; neurotensin; shRNA; ventral tegmental area.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurotensin inhibits glutamate-mediated synaptic inputs onto ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons through the release of the endocannabinoid 2-AG.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Nov;63(6):983-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.07.037. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22884466
-
Ventral tegmental area neurotensin signaling links the lateral hypothalamus to locomotor activity and striatal dopamine efflux in male mice.Endocrinology. 2015 May;156(5):1692-700. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1986. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25734363 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol blocks the reversal of prolonged dopamine inhibition of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Nov;36(11):1913-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01814.x. Epub 2012 May 2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22551160 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of cannabinoid CB2 receptor-mediated reduction of dopamine neuronal excitability in mouse ventral tegmental area.EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:225-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.040. Epub 2019 Apr 3. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30952618 Free PMC article.
-
The electrophysiological actions of neurotensin in the central nervous system.Life Sci. 1991;49(14):987-1002. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90300-z. Life Sci. 1991. PMID: 1890928 Review.
Cited by
-
Estradiol increases the sensitivity of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to dopamine and ethanol.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 6;12(11):e0187698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187698. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29107956 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Dysregulation of Cholesterol Synthesis Underlies Hyposensitivity to GABA in the Ventral Tegmental Area During Acute Alcohol Withdrawal.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 1;95(3):275-285. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.07.018. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37562519 Free PMC article.
-
Phorbol ester reduces ethanol excitation of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area: involvement of protein kinase C theta.Front Integr Neurosci. 2013 Dec 25;7:96. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2013.00096. eCollection 2013. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24399942 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol antagonizes P2X4 receptors in ventral tegmental area neurons.Neuroreport. 2020 Aug 12;31(12):936-941. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001504. Neuroreport. 2020. PMID: 32658126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borghese C. M., Werner D. F., Topf N., Baron N. V., Henderson L. A., Boehm S. L., et al. (2006). An isoflurane- and alcohol-insensitive mutant GABA(A) receptor alpha(1) subunit with near-normal apparent affinity for GABA: characterization in heterologous systems and production of knockin mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 319, 208–21810.1124/jpet.106.104406 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brodie M. S., McElvain M. A., Bunney E. B., Appel S. B. (1999). Pharmacological reduction of small conductance calcium-activated potassium current (SK) potentiates the excitatory effect of ethanol on ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 325–333 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

