The oncogene metadherin modulates the apoptotic pathway based on the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand) in breast cancer
- PMID: 23408429
- PMCID: PMC3611009
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.395913
The oncogene metadherin modulates the apoptotic pathway based on the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand) in breast cancer
Abstract
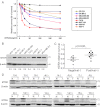
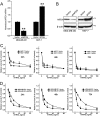
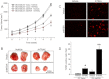
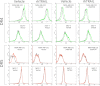
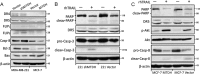
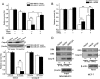
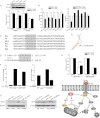
Metadherin (MTDH), the newly discovered gene, is overexpressed in more than 40% of breast cancers. Recent studies have revealed that MTDH favors an oncogenic course and chemoresistance. With a number of breast cancer cell lines and breast tumor samples, we found that the relative expression of MTDH correlated with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) sensitivity in breast cancer. In this study, we found that knockdown of endogenous MTDH cells sensitized the MDA-MB-231 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo. Conversely, stable overexpression of MTDH in MCF-7 cells enhanced cell survival with TRAIL treatment. Mechanically, MTDH down-regulated caspase-8, decreased caspase-8 recruitment into the TRAIL death-inducing signaling complex, decreased caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 processing, increased Bcl-2 expression, and stimulated TRAIL-induced Akt phosphorylation, without altering death receptor status. In MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, sensitization to TRAIL upon MTDH down-regulation was inhibited by the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk (benzyloxycarbonyl-VAD-fluoromethyl ketone), suggesting that MTDH depletion stimulates activation of caspases. In MCF-7 breast cancer cells, resistance to TRAIL upon MTDH overexpression was abrogated by depletion of Bcl-2, suggesting that MTDH-induced Bcl-2 expression contributes to TRAIL resistance. We further confirmed that MTDH may control Bcl-2 expression partly by suppressing miR-16. Collectively, our results point to a protective function of MTDH against TRAIL-induced death, whereby it inhibits the intrinsic apoptosis pathway through miR-16-mediated Bcl-2 up-regulation and the extrinsic apoptosis pathway through caspase-8 down-regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Wiley S. R., Schooley K., Smolak P. J., Din W. S., Huang C. P., Nicholl J. K., Sutherland G. R., Smith T. D., Rauch C., Smith C. A., et al. (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3, 673–682 - PubMed
-
- Pitti R. M., Marsters S. A., Ruppert S., Donahue C. J., Moore A., Ashkenazi A. (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12687–12690 - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A., Pai R. C., Fong S., Leung S., Lawrence D. A., Marsters S. A., Blackie C., Chang L., McMurtrey A. E., Hebert A., DeForge L., Koumenis I. L., Lewis D., Harris L., Bussiere J., Koeppen H., Shahrokh Z., Schwall R. H. (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J. Clin. Invest. 104, 155–162 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walczak H., Miller R. E., Ariail K., Gliniak B., Griffith T. S., Kubin M., Chin W., Jones J., Woodward A., Le T., Smith C., Smolak P., Goodwin R. G., Rauch C. T., Schuh J. C., Lynch D. H. (1999) Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 5, 157–163 - PubMed
-
- Newsom-Davis T., Prieske S., Walczak H. (2009) Is TRAIL the holy grail of cancer therapy? Apoptosis 14, 607–623 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

