Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 1B (JARID1B) histone demethylase by a sensitive high throughput screen
- PMID: 23408432
- PMCID: PMC3611010
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.419861
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 1B (JARID1B) histone demethylase by a sensitive high throughput screen
Abstract
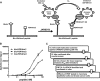
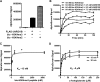
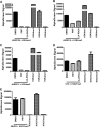
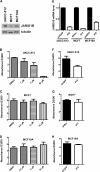
JARID1B (also known as KDM5B or PLU1) is a member of the JARID1 family of histone lysine demethylases responsible for the demethylation of trimethylated lysine 27 in histone H3 (H3K4me3), a mark for actively transcribed genes. JARID1B is overexpressed in several cancers, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and lung cancer. In addition, JARID1B is required for mammary tumor formation in syngeneic or xenograft mouse models. JARID1B-expressing melanoma cells are associated with increased self-renewal character. Therefore, JARID1B represents an attractive target for cancer therapy. Here we characterized JARID1B using a homogeneous luminescence-based demethylase assay. We then conducted a high throughput screen of over 15,000 small molecules to identify inhibitors of JARID1B. From this screen, we identified several known JmjC histone demethylase inhibitors, including 2,4-pyridinedicarboxylic acid and catechols. More importantly, we identified several novel inhibitors, including 2-4(4-methylphenyl)-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one (PBIT), which inhibits JARID1B with an IC50 of about 3 μm in vitro. Consistent with this, PBIT treatment inhibited removal of H3K4me3 by JARID1B in cells. Furthermore, this compound inhibited proliferation of cells expressing higher levels of JARID1B. These results suggest that this novel small molecule inhibitor is a lead compound that can be further optimized for cancer therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Klose R. J., Yan Q., Tothova Z., Yamane K., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Gilliland D. G., Zhang Y., Kaelin W. G., Jr. (2007) The retinoblastoma binding protein RBP2 is an H3K4 demethylase. Cell 128, 889–900 - PubMed
-
- Lee M. G., Norman J., Shilatifard A., Shiekhattar R. (2007) Physical and functional association of a trimethyl H3K4 demethylase and Ring6a/MBLR, a polycomb-like protein. Cell 128, 877–887 - PubMed
-
- Christensen J., Agger K., Cloos P. A., Pasini D., Rose S., Sennels L., Rappsilber J., Hansen K. H., Salcini A. E., Helin K. (2007) RBP2 belongs to a family of demethylases, specific for tri-and dimethylated lysine 4 on histone 3. Cell 128, 1063–1076 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

