Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Bacillus timonensis sp. nov
- PMID: 23408487
- PMCID: PMC3558959
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.2776064
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Bacillus timonensis sp. nov
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Bacillus timonensis sp. nov.Environ Microbiome. 2023 Jun 7;18(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40793-022-00448-8. Environ Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37287068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
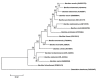
Bacillus timonensis strain MM10403188(T) sp. nov. is the type strain of a proposed new species within the genus Bacillus. This strain, whose genome is described here, was isolated from the fecal flora of a healthy patient. B. timonensis is an aerobic Gram-negative rod shaped bacterium. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. The 4,632,049 bp long genome (1 chromosome but no plasmid) contains 4,610 protein-coding and 74 RNA genes, including 5 rRNA genes.
Keywords: Bacillus timonensis; genome.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Alistipes timonensis sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2012 Jul 30;6(3):315-24. doi: 10.4056/sigs.2685971. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Stand Genomic Sci. 2012. PMID: 23408657 Free PMC article.
-
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Peptoniphilus timonensis sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2012 Oct 10;7(1):1-11. doi: 10.4056/sigs.2956294. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Stand Genomic Sci. 2012. PMID: 23449949 Free PMC article.
-
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Enorma timonensis sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2014 Feb 15;9(3):970-86. doi: 10.4056/sigs.4878632. eCollection 2014 Jun 15. Stand Genomic Sci. 2014. PMID: 25197477 Free PMC article.
-
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Bacillus massiliosenegalensis sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2013 Jun 5;8(2):264-78. doi: 10.4056/sigs.3496989. eCollection 2013. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013. PMID: 23991258 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence and description of Bacteroides timonensis sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2014 Mar 15;9(3):1181-97. doi: 10.4056/sigs.5389564. eCollection 2014 Jun 15. Stand Genomic Sci. 2014. PMID: 25197491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Grimontia indica AK16(T), sp. nov., isolated from a seawater sample reports the presence of pathogenic genes similar to Vibrio genus.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85590. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085590. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465608 Free PMC article.
-
Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Kallipyga massiliensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Clostridiales Incertae Sedis XI.Stand Genomic Sci. 2013 Jul 30;8(3):500-15. doi: 10.4056/sigs.4047997. eCollection 2013 Jul 30. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013. PMID: 24501634 Free PMC article.
-
Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Anaerococcus pacaensis sp. nov., a new species of anaerobic bacterium.Stand Genomic Sci. 2013 Aug 10;8(3):548-60. doi: 10.4056/sigs.4177252. eCollection 2013 Jul 30. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013. PMID: 24501638 Free PMC article.
-
Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Clostridium dakarense sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2013 Sep 30;9(1):14-27. doi: 10.4056/sigs.4097825. eCollection 2013 Oct 16. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013. PMID: 24501642 Free PMC article.
-
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of Senegalemassilia anaerobia gen. nov., sp. nov.Stand Genomic Sci. 2013 Feb 25;7(3):343-56. doi: 10.4056/sigs.3246665. eCollection 2013. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013. PMID: 24019984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossello-Mora R. DNA-DNA Reassociation Methods Applied to Microbial Taxonomy and Their Critical Evaluation. In: Stackebrandt E (ed), Molecular Identification, Systematics, and population Structure of Prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin, 2006, p. 23-50.
-
- Stackebrandt E, Ebers J. Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 2006; 33:152-155
-
- Lagier JC, El Karkouri K, Nguyen TT, Armougom F, Raoult D, Fournier PE. Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Anaerococcus senegalensis sp. nov. Stand Genomic Sci 2012; 6:116-125 10.4056/sigs.2415480 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

