Association of serum angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2 and angiopoietin-2 to angiopoietin-1 ratio with heart failure in patients with acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 23408510
- PMCID: PMC3570239
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.893
Association of serum angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2 and angiopoietin-2 to angiopoietin-1 ratio with heart failure in patients with acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
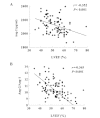
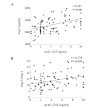
The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of the serum angiopoietin (Ang)-1 and Ang-2 levels and the Ang-2 to Ang-1 ratio (Ang-2/Ang-1) with heart failure (HF) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) during hospitalization. The serum Ang-1 and Ang-2 levels of the AMI patients were measured at admission to hospital. The correlations between serum Ang-1, Ang-2 and Ang-2/Ang-1 with HF were examined. Among 103 patients, 20 developed HF during hospitalization. The serum Ang-2 level and Ang-2/Ang-1 were found to be significantly higher in the patients with HF than in the patients without HF (2,203.1±122.0 vs. 2,102.3±114.4 pg/ml, P=0.001 and 11.4±1.6×10(-2) vs. 10.6±1.1×10(-2), P=0.007, respectively). Serum Ang-2 level and Ang-2/Ang-1 were negatively correlated with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF; r=-0.352, P<0.001 and r=-0.365, P<0.001, respectively) and positively correlated with the natural logarithm of the level of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (LnNT-proBNP, r=0.367, P<0.001 and r=0.304, P=0.003, respectively) and peak cardiac troponin T (cTnT, r=0.421, P<0.001 and r=0.278, P=0.009, respectively). However, the serum Ang-1 level was not found to correlate significantly with LVEF (r= 0.194, P= 0.05), LnNT-proBNP (r=-0.116, P=0.266) or peak cTnT (r=-0.056, P=0.607). In multivariable logistic regression analysis, Ang-2 (P=0.031), Ang-2/Ang-1 (P=0.018) and NT-proBNP (P=0.001) were revealed to be independently associated with HF. The present study reveals that Ang-2 levels and Ang-2/Ang-1 are independent predictors of HF in AMI patients during hospitalization.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; angiopoietin; heart failure.
Figures
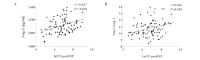
Similar articles
-
Combination of high-sensitivity troponin I and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide predicts future hospital admission for heart failure in high-risk hypertensive patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.Heart Vessels. 2017 Jul;32(7):880-892. doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-0948-9. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Heart Vessels. 2017. PMID: 28154958
-
[Prognostic value of N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide on all-cause mortality in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 24;47(11):875-881. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.11.005. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31744276 Chinese.
-
C-Reactive Protein and N-Terminal Pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels Correlate With Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients With Heart Failure Across a Wide Range of Ejection Fraction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Dec 21;5:178. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00178. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 30619885 Free PMC article.
-
N-Terminal Pro B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Levels Are Related to the Extent of Hibernating Myocardium in Patients With Ischemic Heart Failure.Can J Cardiol. 2017 Nov;33(11):1478-1488. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Can J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28966019
-
Biomarkers and diagnostics in heart failure.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2442-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23313577 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating angiogenic factors in diabetes patients in a tertiary hospital in Ghana.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Oct 10;15:44. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0267-1. eCollection 2016. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27777900 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cardiokines in Heart Diseases: Beneficial or Detrimental?Biomed Res Int. 2018 Mar 18;2018:8207058. doi: 10.1155/2018/8207058. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29744364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Angiopoietin-2 level increase differs between polytraumatized patients with and without central nervous system injuries.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19338. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45688-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935720 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial permeability following coronary artery bypass grafting: an observational study on the possible role of angiopoietin imbalance.Crit Care. 2016 Mar 6;20:51. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1238-0. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 26951111 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Angiopoietin Factor 2 Levels Are Correlated with Better Cardiac Function and Prognosis in Valvular Heart Disease.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 Feb 10;38(1):104-109. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2021-0364. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 35657310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Task Force on the management of ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2569–2619. - PubMed
-
- Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996;87:1161–1169. - PubMed
-
- Thomas M, Augustin HG. The role of the Angiopoietins in vascular morphogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2009;12:125–137. - PubMed
-
- Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, et al. Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science. 1997;277:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Post S, Peeters W, Busser E, et al. Balance between angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 is in favor of angiopoietin-2 in atherosclerotic plaques with high microvessel density. J Vasc Res. 2008;45:244–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
