Broader Autism Phenotype in Iranian Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders vs. Normal Children
- PMID: 23408558
- PMCID: PMC3570573
Broader Autism Phenotype in Iranian Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders vs. Normal Children
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present study was to compare the broader autism phenotype in Iranian parents of children with autism spectrum disorders and parents of typically developing children.
Method: Parents of children with ASD and parents of typically developing children were asked to complete the Persian version of the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ). In the ASD group, families included 204 parents (96 fathers and 108 mothers) of children diagnosed as having autism (Autistic Disorder, or AD) (n=124), Asperger Syndrome (AS) or High Functioning Autism (HFA) (n=48) and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS) (n=32) by psychiatrists based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-4thedition (DSM-IV-TR) criteria. In the control group, 210 (108 fathers and 102 mothers) parents of typically developing children. Parents of typically developing children were selected from four primary schools. Based on family reports, their children did not have any psychiatric problems. Total AQ score and each of the 5 subscales were analyzed using two-way ANOVAs with sex and group as factors.
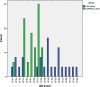
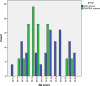
Results: The mean age of ASD fathers was 40.6 years (SD=5.96; range 31-54), and of ASD mothers was 34.7 years (SD=4.55; range 28-45). The mean age of control fathers was 37 years (SD=4.6; range 29-45) and of control mothers was 34.11 years (SD=4.86; range 28-45). Group differences were found in age (p ‹ 0/001). On total AQ, a main effect for group and sex was found. ASD parents scored higher than controls (F(1,410)=77.876, P ‹ 0/001) and males scored higher than females (F(1,410)=23.324, P ‹ 0/001). Also, Group by Sex interaction was significant (F(1,410)=4.986, P ‹ 0/05). Results of MANOVA analysis displayed significant differences between ASD's subgroups on total AQ and subscales scores (F (15, 1121)=13.924, p < 0.0005; Wilk's Lambda= 0.624, partial =0.145). Pairwise comparisons between ASD's subgroups and Normal group showed that mean scores for the Asperger group are significantly more than other groups in total AQ, attention switching and communication subscales (p < 0.05). The frequencies of BAP (X^2=52.721 (DF=1), P ‹ 0/001), MAP (X^2=17.133 (DF=1), P ‹ 0/001) and NAP (X^2=12.722 (DF=1), P ‹ 0/001) in ASD parents were significantly more than control parents. The frequencies of Broader Autism Phenotype (BAP) (X^2=3.842 (DF=1), P›0/05) and Medium Autism phenotype (MAP) (X^2=0.060 (DF=1), P›0/05) did not significantly differ in ASD fathers and mothers, but the proportion of fathers in Narrow Autism Phenotype(NAP) range was more than mothers (X2=14.344, P ‹ 0/001).
Conclusion: Results of the present study revealed that parents of children with ASD scored significantly higher than control parents on total AQ and its subscales and the rates of BAP, MAP and NAP were higher in ASD parents than in controls. In addition, in ASD's subgroups, the parents of Asperger children scored significantly more than other subgroups (Autism and PDD-nos) and the normal group on total AQ and some subscales.
Keywords: Autistic disorder; Child; Iran; Parents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Asperger Syndrome.2024 Feb 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Feb 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32491480 Free Books & Documents.
-
Broader autistic phenotype in parents of children with autism: Autism Spectrum Quotient-Turkish version.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013 Jan;67(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12005. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23331285
-
Defining the broader, medium and narrow autism phenotype among parents using the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ).Mol Autism. 2010 Jun 17;1(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-1-10. Mol Autism. 2010. PMID: 20678260 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
-
Autism and other pervasive developmental disorders: exploring the dimensional view.Can J Psychiatry. 1998 Aug;43(6):589-95. doi: 10.1177/070674379804300607. Can J Psychiatry. 1998. PMID: 9729686 Review.
Cited by
-
Broader autism phenotype in parents of children with autism: a systematic review of percentage estimates.J Child Fam Stud. 2018 Jun;27(6):1705-1720. doi: 10.1007/s10826-018-1026-3. Epub 2018 Feb 22. J Child Fam Stud. 2018. PMID: 29731598 Free PMC article.
-
An examination of autism spectrum traits in adolescents with anorexia nervosa and their parents.Mol Autism. 2014 Dec 20;5(1):56. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-5-56. eCollection 2014. Mol Autism. 2014. PMID: 25553237 Free PMC article.
-
Mothers of autistic children: lower plasma levels of oxytocin and Arg-vasopressin and a higher level of testosterone.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 25;8(9):e74849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074849. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086383 Free PMC article.
-
Autistic traits in couple dyads as a predictor of anxiety spectrum symptoms.J Autism Dev Disord. 2014 Nov;44(11):2949-63. doi: 10.1007/s10803-014-2151-5. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014. PMID: 24907095
-
Measuring autistic traits in the general population: a systematic review of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) in a nonclinical population sample of 6,900 typical adult males and females.Mol Autism. 2015 Jan 14;6:2. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-6-2. eCollection 2015. Mol Autism. 2015. PMID: 25874074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charman T, Baird G. Practitioner review: Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in 2- and 3-year-old children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2002;43:289–305. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SY. Diagnosis of autism before the age of 3. International Review of Mental Retardation. 2001;23:1–31.
-
- Akhondzadeh S, Erfani S, Mohammadi MR, Tehrani-Doost M, Amini H, Gudarzi SS, et al. Cyproheptadine in the treatment of autistic disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2004;29:145–150. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous