A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II)
- PMID: 23408728
- PMCID: PMC3739931
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.20309
A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II)
Abstract
Objective: To examine the effects of naltrexone/bupropion (NB) combination therapy on weight and weight-related risk factors in overweight and obese participants.
Design and methods: CONTRAVE Obesity Research-II (COR-II) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 1,496 obese (BMI 30-45 kg/m(2) ) or overweight (27-45 kg/m(2) with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension) participants randomized 2:1 to combined naltrexone sustained-release (SR) (32 mg/day) plus bupropion SR (360 mg/day) (NB32) or placebo for up to 56 weeks. The co-primary endpoints were percent weight change and proportion achieving ≥ 5% weight loss at week 28.
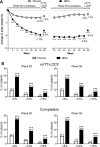
Results: Significantly (P < 0.001) greater weight loss was observed with NB32 versus placebo at week 28 (-6.5% vs. -1.9%) and week 56 (-6.4% vs. -1.2%). More NB32-treated participants (P < 0.001) experienced ≥ 5% weight loss versus placebo at week 28 (55.6% vs. 17.5%) and week 56 (50.5% vs. 17.1%). NB32 produced greater improvements in various cardiometabolic risk markers, participant-reported weight-related quality of life, and control of eating. The most common adverse event with NB was nausea, which was generally mild to moderate and transient. NB was not associated with increased events of depression or suicidality versus placebo.
Conclusion: NB represents a novel pharmacological approach to the treatment of obesity, and may become a valuable new therapeutic option.
Copyright © 2013 The Obesity Society.
Figures
References
-
- Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults, 1999-2002. JAMA. 2004;291:2847–28s50. - PubMed
-
- Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, et al. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1138–1145. - PubMed
-
- NHLBI/NIDDK. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; 1998. - PubMed
-
- Grodstein F, Levine R, Troy L, Spencer T, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ. Three-year follow-up of participants in a commercial weight loss program. Can you keep it off? Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:1302–1306. - PubMed
-
- Riddle M. Combining sulfonylureas and other oral agents. Am J Med. 2000;108(Suppl 6a):15S–22S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

