Development of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen using novel monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 23408744
- PMCID: PMC3558164
Development of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen using novel monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
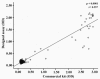
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is the 10th leading cause of death worldwide. The most important diagnostic and screening marker for HBV infection is Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), and the most widely used HBsAg screening test is Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). In this study, an ELISA assay has been developed for detection of HBsAg using two novel monoclonal antibodies (mAb) as capture layer and a polyclonal biotinylated Ab as detector phase. We evaluated the sensitivity, specificity, detection limit, seroconversion time, positive and negative predictive values and reproducibility of our assay with standard panels and different serum samples. The results were compared with a well established commercial kit. Both assays showed similar detection limit values of 0.5 to 0.7 ng/ml and the same seroconversion periods of 42 and 65 days for "ad" and "ay" serotypes of HBsAg, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of the assay were 98.98% and 99.6%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive values of our assay were also calculated as 99.49% and 99.2%, respectively. Analysis of reproducibility of the present assay demonstrated 3.96% and 5.85% intra-and inter-assay coefficient of variations, respectively, which were less than those obtained by the commercial kit. There was a highly significant correlation between our designed assay and the commercial ELISA kit (p < 0.0001, r = 0.957). Altogether, our results indicate that the designed assay is comparable to the commercial kit in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and reproducibility and could be employed for diagnosis of HBV infection in blood samples.
Keywords: ELISA; Hepatitis B; Hepatitis B surface antigens; Monoclonal antibody.
Figures


References
-
- Chen DS. Toward elimination and eradication of hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(1):19–25. - PubMed
-
- Yokosuka O, Arai M. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus: effect of nucleotide substitutions on the clinical features of chronic hepatitis B. Med Mol Morphol. 2006;39(3):113–120. - PubMed
-
- Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection-natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(11):1118–1129. - PubMed
-
- Hatzakis A, Magiorkinis E, Haida C. HBV virological assessment. J Hepatol. 2006;44(1):S71–S76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
