Sensory deprivation during early development causes an increased exploratory behavior in a whisker-dependent decision task
- PMID: 23408764
- PMCID: PMC3568787
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.102
Sensory deprivation during early development causes an increased exploratory behavior in a whisker-dependent decision task
Abstract
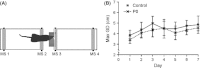
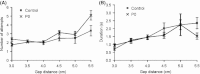
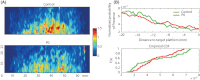
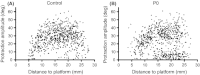
Stimulation of sensory pathways is important for the normal development of cortical sensory areas, and impairments in the normal development can have long-lasting effect on animal's behavior. In particular, disturbances that occur early in development can cause permanent changes in brain structure and function. The behavioral effect of early sensory deprivation was studied in the mouse whisker system using a protocol to induce a 1-week sensory deprivation immediately after birth. Only two rows of whiskers were spared (C and D rows), and the rest were deprived, to create a situation where an unbalanced sensory input, rather than a complete loss of input, causes a reorganization of the sensory map. Sensory deprivation increased the barrel size ratio of the spared CD rows compared with the deprived AB rows; thus, the map reorganization is likely due, at least in part, to a rewiring of thalamocortical projections. The behavioral effect of such a map reorganization was investigated in the gap-crossing task, where the animals used a whisker that was spared during the sensory deprivation. Animals that had been sensory deprived performed equally well with the control animals in the gap-crossing task, but were more active in exploring the gap area and consequently made more approaches to the gap - approaches that on average were of shorter duration. A restricted sensory deprivation of only some whiskers, although it does not seem to affect the overall performance of the animals, does have an effect on their behavioral strategy on executing the gap-crossing task.
Keywords: Barrel cortex; development; gap-cross; sensory deprivation; whisker tracking.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong-James M, Callahan CA. Thalamo-cortical processing of vibrissal information in the rat. II. Spatiotemporal convergence in the thalamic ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPm) and its relevance to generation of receptive fields of S1 cortical “barrel” neurones. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991;303:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Barneoud P, Gyger M, Andres F, van der Loos H. Vibrissa-related behavior in mice: transient effect of ablation of the barrel cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 1991;44:87–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

