Direct binding of the Kex2p cytosolic tail to the VHS domain of yeast Gga2p facilitates TGN to prevacuolar compartment transport and is regulated by phosphorylation
- PMID: 23408788
- PMCID: PMC3571872
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-11-0843
Direct binding of the Kex2p cytosolic tail to the VHS domain of yeast Gga2p facilitates TGN to prevacuolar compartment transport and is regulated by phosphorylation
Abstract
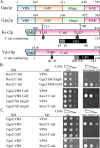
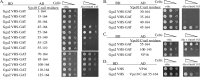
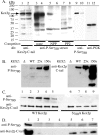
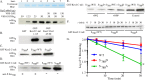
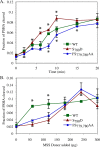
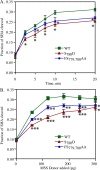
Human Golgi-localized, γ-ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding proteins (Ggas) bind directly to acidic dileucine sorting motifs in the cytosolic tails (C-tails) of intracellular receptors. Despite evidence for a role in recruiting ubiquitinated cargo, it remains unclear whether yeast Ggas also function by binding peptide-sorting signals directly. Two-hybrid analysis shows that the Gga1p and Gga2p Vps27, Hrs, Stam (VHS) domains both bind a site in the Kex2p C-tail and that the Gga2p VHS domain binds a site in the Vps10p C-tail. Binding requires deletion of an apparently autoinhibitory sequence in the Gga2p hinge. Ser(780) in the Kex2p C-tail is crucial for binding: an Ala substitution blocks but an Asp substitution permits binding. Biochemical assays using purified Gga2p VHS-GGA and TOM1 (GAT) and glutathione S-transferase-Kex2p C-tail fusions show that Gga2p binds directly to the Kex2p C-tail, with relative affinities Asp(780) > Ser(780) > Ala(780). Affinity-purified antibody against a peptide containing phospho-Ser-(780) recognizes wild-type Kex2p but not S(780)A Kex2p, showing that Ser(780) is phosphorylated in vivo; phosphorylation of Ser(780) is up-regulated by cell wall-damaging drugs. Finally, mutation of Ser(780) alters trafficking of Kex2p both in vivo and in cell-free trans-Golgi network (TGN)-prevacuolar compartment (PVC) transport. Thus yeast Gga adaptors facilitate TGN-PVC transport by direct binding of noncanonical phosphoregulated Gga-binding sites in cargo molecules.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Yeast Golgi-localized, gamma-Ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding proteins are but adaptor protein-1 is not required for cell-free transport of membrane proteins from the trans-Golgi network to the prevacuolar compartment.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Nov;19(11):4826-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0442. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18784256 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free transport from the trans-golgi network to late endosome requires factors involved in formation and consumption of clathrin-coated vesicles.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4442-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412553200. Epub 2004 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15572353
-
SOI1 encodes a novel, conserved protein that promotes TGN-endosomal cycling of Kex2p and other membrane proteins by modulating the function of two TGN localization signals.J Cell Biol. 1997 Oct 6;139(1):23-36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.1.23. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9314526 Free PMC article.
-
Cargo Sorting at the trans-Golgi Network for Shunting into Specific Transport Routes: Role of Arf Small G Proteins and Adaptor Complexes.Cells. 2019 Jun 3;8(6):531. doi: 10.3390/cells8060531. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31163688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GGA proteins: key players in protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network.Eur J Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;83(6):257-62. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00374. Eur J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15511083 Review.
Cited by
-
The Vps13p-Cdc31p complex is directly required for TGN late endosome transport and TGN homotypic fusion.J Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;216(2):425-439. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201606078. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28122955 Free PMC article.
-
COPI selectively drives maturation of the early Golgi.Elife. 2015 Dec 28;4:e13232. doi: 10.7554/eLife.13232. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26709839 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved role for Gga proteins in phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase localization to the trans-Golgi network.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 28;114(13):3433-3438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615163114. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28289207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abazeed ME, Blanchette JM, Fuller RS. Cell-free transport from the trans-Golgi network to late endosome requires factors involved in formation and consumption of clathrin-coated vesicles. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:4442–4450. - PubMed
-
- Abazeed ME, Fuller RS. Yeast Golgi-localized, gamma-Ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding proteins are but adaptor protein-1 is not required for cell-free transport of membrane proteins from the trans-Golgi network to the prevacuolar compartment. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:4826–4836. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanchette JM, Abazeed ME, Fuller RS. Cell-free reconstitution of transport from the trans-Golgi network to the late endosome/prevacuolar compartment. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:48767–48773. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino JS. The GGA proteins: adaptors on the move. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

