Antagonism versus cooperativity with TALE cofactors at the base of the functional diversification of Hox protein function
- PMID: 23408901
- PMCID: PMC3567137
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003252
Antagonism versus cooperativity with TALE cofactors at the base of the functional diversification of Hox protein function
Abstract
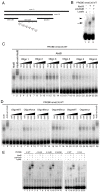
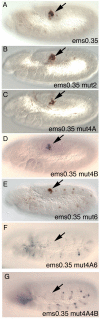
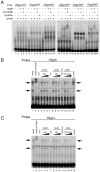
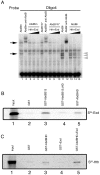
Extradenticle (Exd) and Homothorax (Hth) function as positive transcriptional cofactors of Hox proteins, helping them to bind specifically their direct targets. The posterior Hox protein Abdominal-B (Abd-B) does not require Exd/Hth to bind DNA; and, during embryogenesis, Abd-B represses hth and exd transcription. Here we show that this repression is necessary for Abd-B function, as maintained Exd/Hth expression results in transformations similar to those observed in loss-of-function Abd-B mutants. We characterize the cis regulatory module directly regulated by Abd-B in the empty spiracles gene and show that the Exd/Hth complex interferes with Abd-B binding to this enhancer. Our results suggest that this novel Exd/Hth function does not require the complex to bind DNA and may be mediated by direct Exd/Hth binding to the Abd-B homeodomain. Thus, in some instances, the main positive cofactor complex for anterior Hox proteins can act as a negative factor for the posterior Hox protein Abd-B. This antagonistic interaction uncovers an alternative way in which MEIS and PBC cofactors can modulate Abd-B like posterior Hox genes during development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
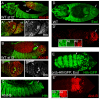
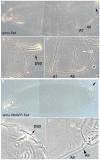
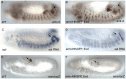
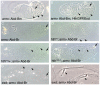
References
-
- Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W (2005) Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat Rev Genet 6: 893–904. - PubMed
-
- Hueber SD, Weiller GF, Djordjevic MA, Frickey T (2010) Improving Hox protein classification across the major model organisms. PLoS ONE 5: e10820 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010820. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merabet S, Hudry B, Saadaoui M, Graba Y (2009) Classification of sequence signatures: a guide to Hox protein function. Bioessays 31: 500–511. - PubMed
-
- Hombría JC-G, Rivas ML, Sotillos S (2009) Genetic control of morphogenesis- Hox induced organogenesis of the posterior spiracles. Int J Dev Biol 53: 1349–1358. - PubMed
-
- Hu N, Castelli-Gair J (1999) Study of the posterior spiracles of Drosophila as a model to understand the genetic and cellular mechanisms controlling morphogenesis. Developmental Biology 214: 197–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

