Single transmembrane peptide DinQ modulates membrane-dependent activities
- PMID: 23408903
- PMCID: PMC3567139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003260
Single transmembrane peptide DinQ modulates membrane-dependent activities
Abstract
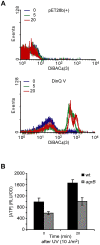
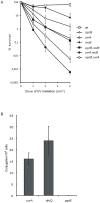
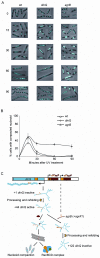
The functions of several SOS regulated genes in Escherichia coli are still unknown, including dinQ. In this work we characterize dinQ and two small RNAs, agrA and agrB, with antisense complementarity to dinQ. Northern analysis revealed five dinQ transcripts, but only one transcript (+44) is actively translated. The +44 dinQ transcript translates into a toxic single transmembrane peptide localized in the inner membrane. AgrB regulates dinQ RNA by RNA interference to counteract DinQ toxicity. Thus the dinQ-agr locus shows the classical features of a type I TA system and has many similarities to the tisB-istR locus. DinQ overexpression depolarizes the cell membrane and decreases the intracellular ATP concentration, demonstrating that DinQ can modulate membrane-dependent processes. Augmented DinQ strongly inhibits marker transfer by Hfr conjugation, indicating a role in recombination. Furthermore, DinQ affects transformation of nucleoid morphology in response to UV damage. We hypothesize that DinQ is a transmembrane peptide that modulates membrane-dependent activities such as nucleoid compaction and recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
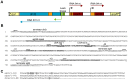
 ) and stop (
) and stop ( ) for dinQ, agrA and agrB. AgrAB repeat sequences are shadowed. (C) Alignment of agrA/agrB sequences antisense to dinQ. The agrAB repeat of dinQ is antisense to sequences in the agrA and agrB transcripts.
) for dinQ, agrA and agrB. AgrAB repeat sequences are shadowed. (C) Alignment of agrA/agrB sequences antisense to dinQ. The agrAB repeat of dinQ is antisense to sequences in the agrA and agrB transcripts.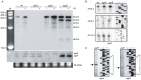
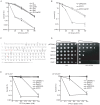
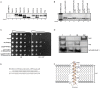
References
-
- Fernandez De Henestrosa AR, Ogi T, Aoyagi S, Chafin D, Hayes JJ, Ohmori H, et al. (2000) Identification of additional genes belonging to the LexA regulon in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 35: 1560–1572. - PubMed
-
- Zuber P (2001) A peptide profile of the Bacillus subtilis genome. Peptides 22: 1555–1577 doi:DOI:10.1016/S0196-9781(01)00492-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ibrahim M, Nicolas P, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Monnet V, et al. (2007) A genome-wide survey of short coding sequences in streptococci. Microbiology 153: 3631–3644. - PubMed
-
- Alix E, Blanc-Potard ABa (2009) Hydrophobic peptides: novel regulators within bacterial membrane. Mol Microbiol 72: 5–1110.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06626.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

