Regulation of Drosophila metamorphosis by xenobiotic response regulators
- PMID: 23408904
- PMCID: PMC3567155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003263
Regulation of Drosophila metamorphosis by xenobiotic response regulators
Abstract
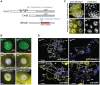
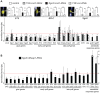
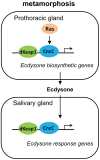
Mammalian Nrf2-Keap1 and the homologous Drosophila CncC-dKeap1 protein complexes regulate both transcriptional responses to xenobiotic compounds as well as native cellular and developmental processes. The relationships between the functions of these proteins in xenobiotic responses and in development were unknown. We investigated the genes regulated by CncC and dKeap1 during development and the signal transduction pathways that modulate their functions. CncC and dKeap1 were enriched within the nuclei in many tissues, in contrast to the reported cytoplasmic localization of Keap1 and Nrf2 in cultured mammalian cells. CncC and dKeap1 occupied ecdysone-regulated early puffs on polytene chromosomes. Depletion of either CncC or dKeap1 in salivary glands selectively reduced early puff gene transcription. CncC and dKeap1 depletion in the prothoracic gland as well as cncC(K6/K6) and dKeap1(EY5/EY5) loss of function mutations in embryos reduced ecdysone-biosynthetic gene transcription. In contrast, dKeap1 depletion and the dKeap1(EY5/EY5) loss of function mutation enhanced xenobiotic response gene transcription in larvae and embryos, respectively. Depletion of CncC or dKeap1 in the prothoracic gland delayed pupation by decreasing larval ecdysteroid levels. CncC depletion suppressed the premature pupation and developmental arrest caused by constitutive Ras signaling in the prothoracic gland; conversely, constitutive Ras signaling altered the loci occupied by CncC on polytene chromosomes and activated transcription of genes at these loci. The effects of CncC and dKeap1 on both ecdysone-biosynthetic and ecdysone-regulated gene transcription, and the roles of CncC in Ras signaling in the prothoracic gland, establish the functions of these proteins in the neuroendocrine axis that coordinates insect metamorphosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Visualization of the Drosophila dKeap1-CncC interaction on chromatin illumines cooperative, xenobiotic-specific gene activation.Development. 2014 Aug;141(16):3277-88. doi: 10.1242/dev.110528. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Development. 2014. PMID: 25063457 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling: regulation of development and xenobiotic response using distinct mechanisms.Fly (Austin). 2014;8(1):7-12. doi: 10.4161/fly.27007. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Fly (Austin). 2014. PMID: 24406335 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Keap1 xenobiotic response factor regulates developmental transcription through binding to chromatin.Dev Biol. 2022 Jan;481:139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.10.003. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34662537 Free PMC article.
-
What goes up must come down: transcription factors have their say in making ecdysone pulses.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013;103:35-71. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385979-2.00002-2. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23347515 Review.
-
Ecdysone signaling cascade and regulation of Drosophila metamorphosis.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996;33(3-4):231-44. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1996)33:3/4<231::AID-ARCH5>3.0.CO;2-V. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8913033 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of the Genomic Loci That Are Bound by Specific Multiprotein Complexes by Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Analysis on Drosophila Polytene Chromosomes.Methods Enzymol. 2017;589:429-455. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28336073 Free PMC article.
-
INO80-dependent regression of ecdysone-induced transcriptional responses regulates developmental timing in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2014 Mar 15;387(2):229-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24468295 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of the Drosophila dKeap1-CncC interaction on chromatin illumines cooperative, xenobiotic-specific gene activation.Development. 2014 Aug;141(16):3277-88. doi: 10.1242/dev.110528. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Development. 2014. PMID: 25063457 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Roles of Glutathione in Ecdysone Biosynthesis and Antioxidant Function During Larval Development in Drosophila.Genetics. 2017 Dec;207(4):1519-1532. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300391. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 29021278 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with B-type lamin reveals the function of Drosophila Keap1 xenobiotic response factor in nuclear architecture.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Apr 20;51(1):556. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09471-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38642177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taguchi K, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2011) Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells 16: 123–140. - PubMed
-
- Slocum SL, Kensler TW (2011) Nrf2: control of sensitivity to carcinogens. Arch Toxicol 85: 273–284. - PubMed
-
- Padmanabhan B, Tong KI, Ohta T, Nakamura Y, Scharlock M, et al. (2006) Structural basis for defects of Keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol Cell 21: 689–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

