Control of multicellular development by the physically interacting deneddylases DEN1/DenA and COP9 signalosome
- PMID: 23408908
- PMCID: PMC3567183
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003275
Control of multicellular development by the physically interacting deneddylases DEN1/DenA and COP9 signalosome
Abstract
Deneddylases remove the ubiquitin-like protein Nedd8 from modified proteins. An increased deneddylase activity has been associated with various human cancers. In contrast, we show here that a mutant strain of the model fungus Aspergillus nidulans deficient in two deneddylases is viable but can only grow as a filament and is highly impaired for multicellular development. The DEN1/DenA and the COP9 signalosome (CSN) deneddylases physically interact in A. nidulans as well as in human cells, and CSN targets DEN1/DenA for protein degradation. Fungal development responds to light and requires both deneddylases for an appropriate light reaction. In contrast to CSN, which is necessary for sexual development, DEN1/DenA is required for asexual development. The CSN-DEN1/DenA interaction that affects DEN1/DenA protein levels presumably balances cellular deneddylase activity. A deneddylase disequilibrium impairs multicellular development and suggests that control of deneddylase activity is important for multicellular development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
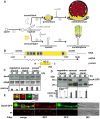
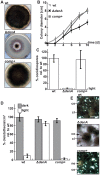
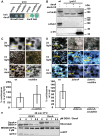

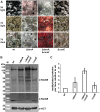


References
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M (2006) Modification of Proteins by Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 425–479. - PubMed
-
- Petroski MD, Deshaies RJ (2005) Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 9–20. - PubMed
-
- von Zeska Kress MR, Harting R, Bayram O, Christmann M, Irmer H, et al... (2012) The COP9 signalosome prevents the accumulation of cullin SCF ubiquitin E3 RING ligases during fungal development. Mol Microbiol, accepted for publication. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto M, Nishida T, Nagayama Y, Yasuda H (2003) Nedd8-modification of Cul1 is promoted by Roc1 as a Nedd8-E3 ligase and regulates its stability. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 301: 392–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

