Duplicate abalone egg coat proteins bind sperm lysin similarly, but evolve oppositely, consistent with molecular mimicry at fertilization
- PMID: 23408913
- PMCID: PMC3567151
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003287
Duplicate abalone egg coat proteins bind sperm lysin similarly, but evolve oppositely, consistent with molecular mimicry at fertilization
Abstract
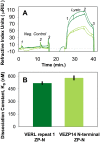
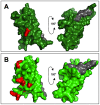
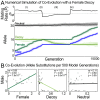
Sperm and egg proteins constitute a remarkable paradigm in evolutionary biology: despite their fundamental role in mediating fertilization (suggesting stasis), some of these molecules are among the most rapidly evolving ones known, and their divergence can lead to reproductive isolation. Because of strong selection to maintain function among interbreeding individuals, interacting fertilization proteins should also exhibit a strong signal of correlated divergence among closely related species. We use evidence of such molecular co-evolution to target biochemical studies of fertilization in North Pacific abalone (Haliotis spp.), a model system of reproductive protein evolution. We test the evolutionary rates (d(N)/d(S)) of abalone sperm lysin and two duplicated egg coat proteins (VERL and VEZP14), and find a signal of co-evolution specific to ZP-N, a putative sperm binding motif previously identified by homology modeling. Positively selected residues in VERL and VEZP14 occur on the same face of the structural model, suggesting a common mode of interaction with sperm lysin. We test this computational prediction biochemically, confirming that the ZP-N motif is sufficient to bind lysin and that the affinities of VERL and VEZP14 are comparable. However, we also find that on phylogenetic lineages where lysin and VERL evolve rapidly, VEZP14 evolves slowly, and vice versa. We describe a model of sexual conflict that can recreate this pattern of anti-correlated evolution by assuming that VEZP14 acts as a VERL mimic, reducing the intensity of sexual conflict and slowing the co-evolution of lysin and VERL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Clark AG, Glanowski S, Nielsen R, Thomas PD, Kejariwal A, et al. (2003) Inferring nonneutral evolution from human-chimp-mouse orthologous gene trios. Science 302: 1960–1963. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen R, Bustamante C, Clark AG, Glanowski S, Sackton TB, et al. (2005) A scan for positively selected genes in the genomes of humans and chimpanzees. PLoS Biol 3: e170 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evolution of genes and genomes on the Drosophila phylogeny. Nature 450: 203–218. - PubMed
-
- Swanson WJ, Vacquier VD (2002) Rapid evolution of reproductive proteins. Nature Reviews Genetics 3: 137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

