Insulin therapy for pre-hyperglycemic beta-cell endoplasmic reticulum crowding
- PMID: 23408938
- PMCID: PMC3567120
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054351
Insulin therapy for pre-hyperglycemic beta-cell endoplasmic reticulum crowding
Abstract
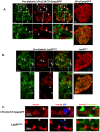
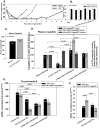
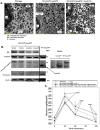
Insulin therapy improves β-cell function in early stages of diabetes by mechanisms that may exceed alleviation of glucotoxicity. In advance type 2 diabetes, hyperglycemia causes β-cell damage and ultimately β-cell loss. At such an advanced stage, therapeutic modalities are often inadequate. Growing evidence indicates that in early stages of type-2 diabetes and some types of monogenic diabetes linked with malfunctioning endoplasmic-reticulum (ER), the β-cell ER fails to process sufficient proinsulin once it becomes overloaded. These changes manifest with ER distention (ER-crowding) and deficiency of secretory granules. We hypothesize that insulin therapy may improves β-cell function by alleviating ER-crowding. To support this hypothesis, we investigated pre-diabetic β-cell changes in hProC(A7)Y-CpepGFP transgenic mice that develop prolonged pre-diabetes due to proinsulin dysmaturation and ER-crowding. We attenuated the β-cell ER proinsulin synthesis with a treat-to-target insulin therapy while avoiding hypoglycemia and weight gain. Alleviation of ER-crowding resulted in temporary improvement in proinsulin maturation, insulin secretion and glucose tolerance. Our observations suggest that alleviation of pre-diabetic ER-crowding using a treat-to-target insulin therapy may improve β-cell function and may prevent further metabolic deterioration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Li Y, Xu W, Liao Z, Yao B, Chen X, et al. (2004) Induction of long-term glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients is associated with improvement of beta-cell function. Diabetes Care 27: 2597–2602. - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Imes S, Wallace C (2004) Short-term intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: 1028–1032. - PubMed
-
- Alvarsson M, Sundkvist G, Lager I, Henricsson M, Berntorp K, et al. (2003) Beneficial effects of insulin versus sulphonylurea on insulin secretion and metabolic control in recently diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 26: 2231–2237. - PubMed
-
- Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, et al. (2008) Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet 371: 1753–1760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

