MUC4 overexpression augments cell migration and metastasis through EGFR family proteins in triple negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23408941
- PMCID: PMC3569463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054455
MUC4 overexpression augments cell migration and metastasis through EGFR family proteins in triple negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Current studies indicate that triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), an aggressive breast cancer subtype, is associated with poor prognosis and an early pattern of metastasis. Emerging evidence suggests that MUC4 mucin is associated with metastasis of various cancers, including breast cancer. However, the functional role of MUC4 remains unclear in breast cancers, especially in TNBCs.
Method: In the present study, we investigated the functional and mechanistic roles of MUC4 in potentiating pathogenic signals including EGFR family proteins to promote TNBC aggressiveness using in vitro and in vivo studies. Further, we studied the expression of MUC4 in invasive TNBC tissue and normal breast tissue by immunostaining.
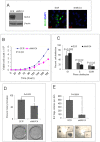
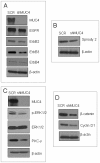
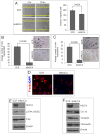
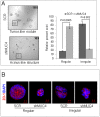
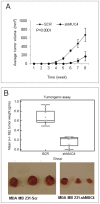
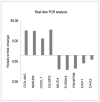
Results: MUC4 promotes proliferation, anchorage-dependent and-independent growth of TNBC cells, augments TNBC cell migratory and invasive potential in vitro, and enhances tumorigenicity and metastasis in vivo. In addition, our studies demonstrated that MUC4 up-regulates the EGFR family of proteins, and augments downstream Erk1/2, PKC-γ, and FAK mediated oncogenic signaling. Moreover, our studies also showed that knockdown of MUC4 in TNBC cells induced molecular changes suggestive of mesenchymal to epithelial transition. We also demonstrated in this study, for the first time, that knockdown of MUC4 was associated with reduced expression of EGFR and ErbB3 (EGFR family proteins) in TNBC cells, suggesting that MUC4 uses an alternative to ErbB2 mechanism to promote aggressiveness. We further demonstrate that MUC4 is differentially over-expressed in invasive TNBC tissues compared to normal breast tissue.
Conclusions: MUC4 mucin expression is associated with TNBC pathobiology, and its knockdown reduced aggressiveness in vitro, and tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. Overall, our findings suggest that MUC4 mucin promotes invasive activities of TNBC cells by altering the expression of EGFR, ErbB2, and ErbB3 molecules and their downstream signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
MUC4 mucin-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition: a novel mechanism for metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells.Oncogene. 2010 Oct 21;29(42):5741-54. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.309. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20697346 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane mucin MUC4 is elevated in breast tumor lymph node metastases relative to matched primary tumors and confers aggressive properties to breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R70. doi: 10.1186/bcr2364. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19761616 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Mucin Muc4 promotes blood cell association with tumor cells and mediates efficient metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 11;37(2):197-207. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.327. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28892049 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Nov;136(2):331-45. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2289-9. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 23073759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of membrane mucin MUC4 in breast cancer metastasis.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2021 Nov 24;29(1):R17-R32. doi: 10.1530/ERC-21-0083. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34726614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular alterations that drive breast cancer metastasis to bone.Bonekey Rep. 2015 Mar 18;4:643. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2015.10. eCollection 2015. Bonekey Rep. 2015. PMID: 25848532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the prognostic significance of MUC4β in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands: An immunohistochemical study.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 14;5(11):e02753. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02753. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844699 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling mucin domains in cancer and metastasis: when protectors become predators.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Sep;39(3):647-659. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09896-5. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32488403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell membrane-anchored MUC4 promotes tumorigenicity in epithelial carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):14147-14157. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13122. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27829225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MUC3A induces PD-L1 and reduces tyrosine kinase inhibitors effects in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr 12;17(7):1671-1681. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.57964. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33994852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN (2008) Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology 52: 108–118. - PubMed
-
- Nofech-Mozes S, Trudeau M, Kahn HK, Dent R, Rawlinson E, et al. (2009) Patterns of recurrence in the basal and non-basal subtypes of triple-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118: 131–137. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan HG, Malmgren JA, Atwood M (2009) T1N0 triple negative breast cancer: risk of recurrence and adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast J 15: 454–460. - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, et al. (2008) Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26: 1275–1281. - PubMed
-
- Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt A, Wu P, et al. (2009) Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N Engl J Med 361: 123–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

