Isoflurane increases neuronal cell death vulnerability by downregulating miR-214
- PMID: 23408966
- PMCID: PMC3568119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055276
Isoflurane increases neuronal cell death vulnerability by downregulating miR-214
Abstract
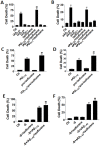
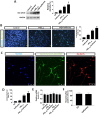
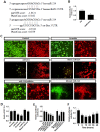
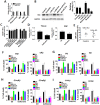
Since accumulating evidence suggests the application of anesthetics may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD), we investigated the cytotoxicity of inhaled general anesthesia in neurons and its underlying mechanism. Using primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons as the study model, here we show that isoflurane increases vulnerability to intracellular or extracellular amyloid β with or without serum deprivation. This isoflurane-induced effect is mediated by the downregulation of miR-214 level that lead to an elevated expression of Bax, a prominent target for miR-214. We conclude that isoflurane increases cell death in the presence of amyloid β by increasing Bax level through downregulating miR-214. Our data provide a new insight for inhaled anesthetics toxicity and indicate a possible mechanistic link between anesthetic application and neurodegenration in AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Halothane increases neuronal cell death vulnerability by downregulating miR-214 and upregulating Bax.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013 Jun 26;6(6):452-60. Print 2013. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23844269 Free PMC article.
-
Desflurane accelerates neuronal cytotoxicity of Aβ by downregulating miR-214.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Oct 25;554:28-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.08.063. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 24021802
-
Long Non-Coding RNA BACE1-AS Modulates Isoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity to Alzheimer's Disease Through Sponging miR-214-3p.Neurochem Res. 2020 Oct;45(10):2324-2335. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03091-2. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32681443
-
The mitochondrial pathway of anesthetic isoflurane-induced apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 5;285(6):4025-4037. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065664. Epub 2009 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20007710 Free PMC article.
-
Vitexin improves neuron apoptosis and memory impairment induced by isoflurane via regulation of miR-409 expression.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 Jan;29(1):135-145. doi: 10.17219/acem/104556. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32011832
Cited by
-
Halothane increases neuronal cell death vulnerability by downregulating miR-214 and upregulating Bax.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013 Jun 26;6(6):452-60. Print 2013. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23844269 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Anesthesia-Induced Neurotoxicity in Animal Models and Neuronal Cultures: a Systematic Review.Neurotox Res. 2020 Mar;37(3):479-490. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00135-6. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31707631
-
Recent progress on the role of non-coding RNA in postoperative cognitive dysfunction.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Oct 13;16:1024475. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1024475. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36313620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of MicroRNA Expression as Biomarker of Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):8376-8391. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01676-9. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31240600
-
miR-365 targets β-arrestin 2 to reverse morphine tolerance in rats.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 6;6:38285. doi: 10.1038/srep38285. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27922111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Price DL, Sisodia SS, Gandy SE (1995) Amyloid beta amyloidosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 8: 268–274. - PubMed
-
- Muravchick S, Smith DS (1995) Parkinsonian symptoms during emergence from general anesthesia. Anesthesiology 82: 305–307. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Baxter M, Yukhananov R, Crosby G (2003) The memory effects of general anesthesia persist for weeks in young and aged rats. Anesth Analg 96: 1004–1009, table of contents. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Crosby CA, Yukhananov R, Crosby G (2004) Impaired acquisition of spatial memory 2 weeks after isoflurane and isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats. Anesth Analg 99: 1393–1397; table of contents. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

