Eomesodermin of atlantic salmon: an important regulator of cytolytic gene and interferon gamma expression in spleen lymphocytes
- PMID: 23409078
- PMCID: PMC3567031
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055893
Eomesodermin of atlantic salmon: an important regulator of cytolytic gene and interferon gamma expression in spleen lymphocytes
Abstract
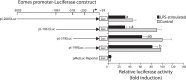
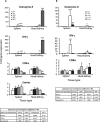
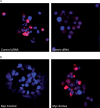
Eomesodermin (Eomes), a T-bet homologue expressed in activated CD8+T cells was recently proposed to act as a master regulator of cytotoxic CD8+ T cell effector function and offers an exciting avenue for future exploration. Here, we have identified and characterized the full-length Atlantic salmon Eomes cDNA (2477 bp). Promoter analysis of the salmon Eomes showed the presence of important putative transcription binding sites like SP1, FOXO, Oct-1, SMAD, STAT, IRF, and Ets-1. The basal core region responsible for the promoter activity was located between base -199 and +59. Quantitative PCR analysis revealed that the Atlantic salmon Eomes was ubiquitously expressed in all the tissues studied but strongly expressed in the ovary, spleen, brain, and the head kidney. Moreover, the involvement of Eomes in Atlantic salmon immune response and its relation with the cytolytic activity was demonstrated by investigating the early time dependent expression profile of Eomes and CD8α followed by high interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and granzyme A expression during challenge with live Aeromonas salmonicida and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis (IPN) virus. Therefore, we further analyzed the regulated expression and function of this transcription factor in spleen lymphocytes. Overexpression of Eomes induced IFN-γ, and granzyme A expression but not perforin expression, whereas small interfering RNA (siRNA) mediated suppression of Eomes expression led to significantly reduced IFN-γ production. Thus, Eomes may be critical in cytolytic gene expression and function in fish similar to mammals. Furthermore, IFN-α, and mitogens induced Eomes expression. Taken together, this is the first study on the promoter activity and regulatory role of Eomes in fish.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Herrmann BG (1992) Action of the Brachyury gene in mouse embryogenesis. Ciba Foundation symposium 165: 78–86. - PubMed
-
- Naiche LA, Harrelson Z, Kelly RG, Papaioannou VE (2005) T-box genes in vertebrate development. Annu Rev Genet 39: 219–239. - PubMed
-
- Pearce EL, Mullen AC, Martins GA, Krawczyk CM, Hutchins AS, et al. (2003) Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor eomesodermin. Science 302: 1041–1043. - PubMed
-
- Russ AP, Wattler S, Colledge WH, Aparicio SA, Carlton MB, et al. (2000) Eomesodermin is required for mouse trophoblast development and mesoderm formation. Nature 404: 95–99. - PubMed
-
- Bruce AE, Howley C, Zhou Y, Vickers SL, Silver LM, et al. (2003) The maternally expressed zebrafish T-box gene eomesodermin regulates organizer formation. Development 130: 5503–5517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

