Unconsciously triggered emotional conflict by emotional facial expressions
- PMID: 23409084
- PMCID: PMC3567040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055907
Unconsciously triggered emotional conflict by emotional facial expressions
Abstract
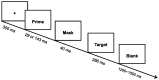
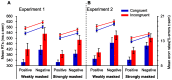
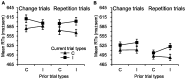
The present study investigated whether emotional conflict and emotional conflict adaptation could be triggered by unconscious emotional information as assessed in a backward-masked affective priming task. Participants were instructed to identify the valence of a face (e.g., happy or sad) preceded by a masked happy or sad face. The results of two experiments revealed the emotional conflict effect but no emotional conflict adaptation effect. This demonstrates that emotional conflict can be triggered by unconsciously presented emotional information, but participants may not adjust their subsequent performance trial-by trial to reduce this conflict.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chiew KS, Braver TS (2010) Exploring emotional and cognitive conflict using upeeded uoluntary uacial expressions. Emotion 10: 842–854. - PubMed
-
- Fenske MJ, Eastwood JD (2003) Modulation of focused fttention by faces expressing emotion: evidence from flanker tasks. Emotion 3: 327–343. - PubMed
-
- Kunde W, Mauer N (2008) Sequential modulations of valence processing in the emotional Stroop task. Exp Psychol 55: 151–156. - PubMed
-
- Williams JMG, Mathews A, MacLeod C (1996) The emotional stroop task and psychopathology. Psychol Bull 120: 3–24. - PubMed
-
- Haas BW, Omura K, Constable RT, Canli T (2006) Interference produced by emotional conflict associated with anterior cingulate activation. Cogn Affect Behav Ne 6: 152–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

