EspO1-2 regulates EspM2-mediated RhoA activity to stabilize formation of focal adhesions in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-infected host cells
- PMID: 23409096
- PMCID: PMC3568036
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055960
EspO1-2 regulates EspM2-mediated RhoA activity to stabilize formation of focal adhesions in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-infected host cells
Abstract
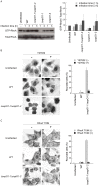
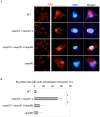
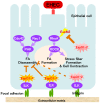
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) Sakai strain encodes two homologous type III effectors, EspO1-1 and EspO1-2. These EspO1s have amino acid sequence homology with Shigella OspE, which targets integrin-linked kinase to stabilize formation of focal adhesions (FAs). Like OspE, EspO1-1 was localized to FAs in EHEC-infected cells, but EspO1-2 was localized in the cytoplasm. An EHEC ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2 double mutant induced cell rounding and FA loss in most of infected cells, but neither the ΔespO1-1 nor ΔespO1-2 single mutant did. These results suggested that EspO1-2 functioned in the cytoplasm by a different mechanism from EspO1-1 and OspE. Since several type III effectors modulate Rho GTPase, which contributes to FA formation, we investigated whether EspO1-2 modulates the function of these type III effectors. We identified a direct interaction between EspO1-2 and EspM2, which acts as a RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Upon ectopic co-expression, EspO1-2 co-localized with EspM2 in the cytoplasm and suppressed EspM2-mediated stress fiber formation. Consistent with these findings, an ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2ΔespM2 triple mutant did not induce cell rounding in epithelial cells. These results indicated that EspO1-2 interacted with EspM2 to regulate EspM2-mediated RhoA activity and stabilize FA formation during EHEC infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subversion of actin dynamics by EspM effectors of attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Jul;10(7):1429-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01136.x. Epub 2008 Mar 5. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18331467 Free PMC article.
-
EspM2 is a RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor.Cell Microbiol. 2010 May 1;12(5):654-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01423.x. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20039879 Free PMC article.
-
The type III secretion system effector EspO of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli inhibits apoptosis through an interaction with HAX-1.Cell Microbiol. 2021 Sep;23(9):e13366. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13366. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Cell Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34021690 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial guanine nucleotide exchange factors SopE-like and WxxxE effectors.Infect Immun. 2010 Apr;78(4):1417-25. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01250-09. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20123714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoskeleton-modulating effectors of enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli: role of EspL2 in adherence and an alternative pathway for modulating cytoskeleton through Annexin A2 function.FEBS J. 2010 Jun;277(11):2403-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07654.x. Epub 2010 Apr 30. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20477868 Review.
Cited by
-
Model of Host-Pathogen Interaction Dynamics Links In Vivo Optical Imaging and Immune Responses.Infect Immun. 2016 Dec 29;85(1):e00606-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00606-16. Print 2017 Jan. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27821583 Free PMC article.
-
Staying out or Going in? The Interplay between Type 3 and Type 5 Secretion Systems in Adhesion and Invasion of Enterobacterial Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 8;21(11):4102. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114102. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32521829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manipulation of Focal Adhesion Signaling by Pathogenic Microbes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 29;22(3):1358. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031358. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Epithelial Cell Shedding on Intestinal Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 9;23(8):4160. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084160. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of Crk adaptor proteins to host cell and bacteria interactions.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:372901. doi: 10.1155/2014/372901. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25506591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frankel G, Phillips AD, Rosenshine I, Dougan G, Kaper JB, et al. (1998) Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: more subversive elements. Mol Microbiol 30: 911–921. - PubMed
-
- Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HL (2004) Pathogenic Escherichia coli . Nat Rev Microbiol 2: 123–140. - PubMed
-
- Hayward RD, Leong JM, Koronakis V, Campellone KG (2006) Exploiting pathogenic Escherichia coli to model transmembrane receptor signalling. Nat Rev Microbiol 4: 358–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

