Relationship of glucocorticoid receptor expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the cochlea of guinea pigs and effects of dexamethasone administration
- PMID: 23409174
- PMCID: PMC3567064
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056323
Relationship of glucocorticoid receptor expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the cochlea of guinea pigs and effects of dexamethasone administration
Abstract
Background: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are widely used to treat sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) and significantly improve hearing. However, GC insensitivity has been observed in some patients of SSNHL.
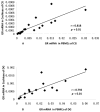
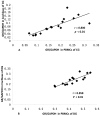
Objective: To study the correlation between GR expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and in the cochlea of guinea pigs at mRNA and protein levels.
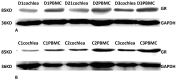
Methods: One group of guinea pigs received dexamethasone (10 mg/kg/day) intraperitoneally for 7 consecutive days (dexamethasone group), and another group of guinea pigs received normal saline (control group). Real time PCR and Western blotting were used to detect the expression of GR mRNA and GR protein in PBMCs and the cochleae.
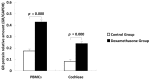
Results: The GR mRNA and GR protein were detected in both PBMCs and the cochlear tissue of guinea pigs. GR mRNA and GR protein levels in PBMCs were positively correlated with those in the cochlea. The expression of GR mRNA and GR protein was significantly increased in the dexamethasone group compared to the control group.
Conclusions: Levels of GR mRNA and GR protein in the PBMCs were positively correlated with those in the cochlea of guinea pigs. Systemic dexamethasone treatment can significantly up-regulate GR expression in PBMCs and in the cochlea. Measurement of the GR level in PBMCs could be used as an indicator of GR level in the cochlea.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Schreiber BE, Agrup C, Haskard DO, Luxon LM (2010) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 375: 1203–1211. - PubMed
-
- Dodson KM, Woodson E, Sismanis A (2004) Intratympanic steroid perfusion for the treatment of Meniere's disease: a retrospective study. Ear Nose Throat J 83: 394–398. - PubMed
-
- Rauch SD (2004) Intratympanic steroids for sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North America 37: 1061–1074. - PubMed
-
- Westerlaken BO, de Kleine E, van der Laan B, Albers F (2007) The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss using pulse therapy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Laryngoscope 117: 684–690. - PubMed
-
- Morawski K, Telischi FF, Bohorquez J, Niemczyk K (2009) Preventing hearing damage using topical dexamethasone during reversible cochlear ischemia: an animal model. Otol Neurotol 30: 851–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

