Stallion sperm transcriptome comprises functionally coherent coding and regulatory RNAs as revealed by microarray analysis and RNA-seq
- PMID: 23409192
- PMCID: PMC3569414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056535
Stallion sperm transcriptome comprises functionally coherent coding and regulatory RNAs as revealed by microarray analysis and RNA-seq
Abstract
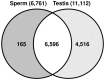
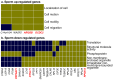
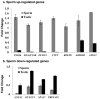
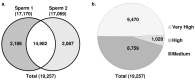
Mature mammalian sperm contain a complex population of RNAs some of which might regulate spermatogenesis while others probably play a role in fertilization and early development. Due to this limited knowledge, the biological functions of sperm RNAs remain enigmatic. Here we report the first characterization of the global transcriptome of the sperm of fertile stallions. The findings improved understanding of the biological significance of sperm RNAs which in turn will allow the discovery of sperm-based biomarkers for stallion fertility. The stallion sperm transcriptome was interrogated by analyzing sperm and testes RNA on a 21,000-element equine whole-genome oligoarray and by RNA-seq. Microarray analysis revealed 6,761 transcripts in the sperm, of which 165 were sperm-enriched, and 155 were differentially expressed between the sperm and testes. Next, 70 million raw reads were generated by RNA-seq of which 50% could be aligned with the horse reference genome. A total of 19,257 sequence tags were mapped to all horse chromosomes and the mitochondrial genome. The highest density of mapped transcripts was in gene-rich ECA11, 12 and 13, and the lowest in gene-poor ECA9 and X; 7 gene transcripts originated from ECAY. Structural annotation aligned sperm transcripts with 4,504 known horse and/or human genes, rRNAs and 82 miRNAs, whereas 13,354 sequence tags remained anonymous. The data were aligned with selected equine gene models to identify additional exons and splice variants. Gene Ontology annotations showed that sperm transcripts were associated with molecular processes (chemoattractant-activated signal transduction, ion transport) and cellular components (membranes and vesicles) related to known sperm functions at fertilization, while some messenger and micro RNAs might be critical for early development. The findings suggest that the rich repertoire of coding and non-coding RNAs in stallion sperm is not a random remnant from spermatogenesis in testes but a selectively retained and functionally coherent collection of RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Krawetz SA (2005) Paternal contribution: new insights and future challenges. Nat Rev Genet 6: 633–642. - PubMed
-
- Galeraud-Denis I, Lambard S, Carreau S (2007) Relationship between chromatin organization, mRNAs profile and human male gamete quality. Asian J Androl 9: 587–592. - PubMed
-
- Betlach CJ, Erickson RP (1973) A unique RNA species from maturing mouse spermatozoa. Nature 242: 114–115. - PubMed
-
- Paul J, Duerksen JD (1975) Chromatin-associated RNA content of heterochromatin and euchromatin. Mol Cell Biochem 9: 9–16. - PubMed
-
- Pessot CA, Brito M, Figueroa J, Concha, II, Yanez A, et al. (1989) Presence of RNA in the sperm nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 158: 272–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

