An extreme wind erosion event of the fresh Eyjafjallajökull 2010 volcanic ash
- PMID: 23409248
- PMCID: PMC3570785
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01257
An extreme wind erosion event of the fresh Eyjafjallajökull 2010 volcanic ash
Abstract
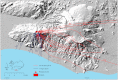
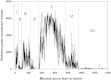
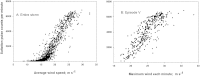
Volcanic eruptions can generate widespread deposits of ash that are subsequently subjected to erosive forces which causes detrimental effects on ecosystems. We measured wind erosion of the freshly deposited Eyjafjallajökull ash at a field site the first summer after the 2010 eruption. Over 30 wind erosion events occurred (June-October) at wind speeds > 10 m s(-1) in each storm with gusts up to 38.7 m s(-1). Surface transport over one m wide transect (surface to 150 cm height) reached > 11,800 kg m(-1) during the most intense storm event with a rate of 1,440 kg m(-1) hr(-1) for about 6½ hrs. This storm is among the most extreme wind erosion events recorded on Earth. The Eyjafjallajökull wind erosion storms caused dust emissions extending several hundred km from the volcano affecting both air quality and ecosystems showing how wind erosion of freshly deposited ash prolongs impacts of volcanic eruptions.
Figures




References
-
- Okin G. S., Gillette D. A. & Herrick J. E. Multi-scale controls on and consequences of aeolian processes in landscape change in arid and semi-arid environments. J. Arid Environ. 65, 253–275 (2006).
-
- Skidmore E. L. in Soil Erosion Research Methods, 2nded. : Wind erosion (ed Lal, R.) 265–293 (Soil and Water Conservation Society, Ankeny, Iowa,1994).
-
- Maun M. A. Adaptations of plants to burial in coastal sand dunes. Can. J. Botany 76, 713–738 (1998).
-
- Pimentel D. & Harvey C. in Ecosystems of Disturbed Ground. Ecosystems of the World:Ecological effects of erosion (ed Walker L. R.) 123–135 (Elsevier Publ., Amsterdam, 1999).
-
- Buzea C., Pacheco I. I. & Robbie K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2, 17–71 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

