The statin-iron nexus: anti-inflammatory intervention for arterial disease prevention
- PMID: 23409890
- PMCID: PMC3673278
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.301163
The statin-iron nexus: anti-inflammatory intervention for arterial disease prevention
Erratum in
- Am J Public Health. 2013 May;103(5):e9
Abstract
Objectives: We postulated the existence of a statin-iron nexus by which statins improve cardiovascular disease outcomes at least partially by countering proinflammatory effects of excess iron stores.
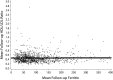
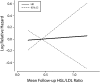
Methods: Using data from a clinical trial of iron (ferritin) reduction in advanced peripheral arterial disease, the Iron and Atherosclerosis Study, we compared effects of ferritin levels versus high-density lipoprotein to low-density lipoprotein ratios (both were randomization variables) on clinical outcomes in participants receiving and not receiving statins.
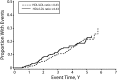
Results: Statins increased high-density lipoprotein to low-density lipoprotein ratios and reduced ferritin levels by noninteracting mechanisms. Improved clinical outcomes were associated with lower ferritin levels but not with improved lipid status.
Conclusions: There are commonalities between the clinical benefits of statins and the maintenance of physiologic iron levels. Iron reduction may be a safe and low-cost alternative to statins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ferritin levels, inflammatory biomarkers, and mortality in peripheral arterial disease: a substudy of the Iron (Fe) and Atherosclerosis Study (FeAST) Trial.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Jun;51(6):1498-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.12.068. Epub 2010 Mar 20. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20304584 Clinical Trial.
-
Atherogenic Lipoprotein Subfractions Determined by Ion Mobility and First Cardiovascular Events After Random Allocation to High-Intensity Statin or Placebo: The Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention: An Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) Trial.Circulation. 2015 Dec 8;132(23):2220-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016857. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 26408274 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Statin effects on both low-density lipoproteins and high-density lipoproteins: is there a dual benefit?Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010 Jan;12(1):14-9. doi: 10.1007/s11883-009-0085-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010. PMID: 20425266 Review.
-
Assessment of Trends in Statin Therapy for Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in US Adults From 2007 to 2016.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Nov 2;3(11):e2025505. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.25505. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33216139 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and future directions in lipid management: emphasizing low-density lipoproteins, high-density lipoproteins, and triglycerides as targets for therapy.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010 Mar 3;6:73-85. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s8725. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010. PMID: 20234782 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential hazards of recent trends in liberal iron use for renal anemia.Clin Kidney J. 2020 Aug 21;14(1):59-69. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa117. eCollection 2021 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2020. PMID: 33564406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that multiple defects in lipid regulation occur before hyperglycemia during the prodrome of type-2 diabetes.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 3;9(9):e103217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103217. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25184286 Free PMC article.
-
Possible link between statin and iron deficiency anemia: A South Korean nationwide population-based cohort study.Sci Adv. 2023 Oct 27;9(43):eadg6194. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6194. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37889968 Free PMC article.
-
Iron and noncontrast magnetic resonance T2* as a marker of intraplaque iron in human atherosclerosis.J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1556-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Mar 24. J Vasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 24674272 Free PMC article.
-
Iron: protector or risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Still controversial.Nutrients. 2013 Jul 1;5(7):2384-404. doi: 10.3390/nu5072384. Nutrients. 2013. PMID: 23857219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Last AR, Ference JD, Falleroni J. Pharmacologic treatment of hyperlipidemia. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84(5):551–558 - PubMed
-
- The Long-Term Intervention With Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(19):1349–1357 - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Rosuvastatin for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm200128.htm. Accessed November 20, 2012.
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FAet al.JUPITER Study Group Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(21):2195–2207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

