The CaMKII/NMDAR complex as a molecular memory
- PMID: 23410178
- PMCID: PMC3582596
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-10
The CaMKII/NMDAR complex as a molecular memory
Abstract
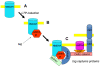
CaMKII is a major synaptic protein that is activated during the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) by the Ca2+ influx through NMDARs. This activation is required for LTP induction, but the role of the kinase in the maintenance of LTP is less clear. Elucidating the mechanisms of maintenance may provide insights into the molecular processes that underlie the stability of stored memories. In this brief review, we will outline the criteria for evaluating an LTP maintenance mechanism. The specific hypothesis evaluated is that LTP is maintained by the complex of activated CaMKII with the NMDAR. The evidence in support of this hypothesis is substantial, but further experiments are required, notably to determine the time course and persistence of complex after LTP induction. Additional work is also required to elucidate how the CaMKII/NMDAR complex produces the structural growth of the synapse that underlies late LTP. It has been proposed by Frey and Morris that late LTP involves the setting of a molecular tag during LTP induction, which subsequently allows the activated synapse to capture the proteins responsible for late LTP. However, the molecular processes by which this leads to the structural growth that underlies late LTP are completely unclear. Based on known binding reactions, we suggest the first molecularly specific version of tag/capture hypothesis: that the CaMKII/NMDAR complex, once formed, serves as a tag, which then leads to a binding cascade involving densin, delta-catenin, and N-cadherin (some of which are newly synthesized). Delta-catenin binds AMPA-binding protein (ABP), leading to the LTP-induced increase in AMPA channel content. The addition of postsynaptic N-cadherin, and the complementary increase on the presynaptic side, leads to a trans-synaptically coordinated increase in synapse size (and more release sites). It is suggested that synaptic strength is stored stably through the combined actions of the CaMKII/NMDAR complex and N-cadherin dimers. These N-cadherin pairs have redundant storage that could provide informational stability in a manner analogous to the base-pairing in DNA.
Figures

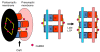
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

