The long-term effectiveness of a lifestyle intervention in severely obese individuals
- PMID: 23410564
- PMCID: PMC3574274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.10.010
The long-term effectiveness of a lifestyle intervention in severely obese individuals
Abstract
Objective: Severe obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥40 kg/m(2)) is a serious public health concern. Although bariatric surgery is an efficacious treatment approach, it is limited in reach; thus, nonsurgical treatment alternatives are needed. We examined the 4-year effects of an intensive lifestyle intervention on body weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors among severely obese, compared with overweight (25 ≤BMI <30), class I (30 ≤BMI <35), and class II obese (35 ≤BMI <40) participants.
Methods: There were 5145 individuals with type 2 diabetes (45-76 years, BMI ≥25 kg/m(2)) randomized to an intensive lifestyle intervention or diabetes support and education. The lifestyle intervention group received a behavioral weight loss program that included group and individual meetings, a ≥10% weight loss goal, calorie restriction, and increased physical activity. Diabetes support and education received a less intense educational intervention. Four-year changes in body weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors were assessed.
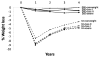
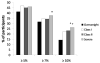
Results: Across BMI categories, 4-year changes in body weight were significantly greater in lifestyle participants compared with diabetes support and education (Ps <.05). At year 4, severely obese lifestyle participants lost 4.9%±8.5%, which was similar to class I (4.8%±7.2%) and class II obese participants (4.4%±7.6%), and significantly greater than overweight participants (3.4%±7.0%; P <.05). Four-year changes in low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, diastolic blood pressure, HbA(1c), and blood glucose were similar across BMI categories in lifestyle participants; however, the severely obese had less favorable improvements in high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (3.1±0.4 mg/dL) and systolic blood pressure (-1.4±0.7 mm Hg) compared with the less obese (Ps <.05).
Conclusion: Lifestyle interventions can result in important long-term weight losses and improvements in cardiovascular disease risk factors among a significant proportion of severely obese individuals.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00017953.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012 Feb 1;307(5):491–497. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein EA, Khavjou OA, Thompson H, et al. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am J Prev Med. 2012 Jun;42(6):563–570. - PubMed
-
- McTigue K, Larson JC, Valoski A, et al. Mortality and cardiac and vascular outcomes in extremely obese women. JAMA. 2006 Jul 5;296(1):79–86. - PubMed
-
- Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999 Oct 27;282(16):1523–1529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK083438/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD006899/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

